Engineered CRO-CD7 CAR-NK cells derived from pluripotent stem cells avoid fratricide and efficiently suppress human T-cell malignancies
- PMID: 40390054
- PMCID: PMC12090657
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-025-01712-3
Engineered CRO-CD7 CAR-NK cells derived from pluripotent stem cells avoid fratricide and efficiently suppress human T-cell malignancies
Abstract
Background: T-cell malignancies are highly aggressive hematological tumors with limited effective treatment options. CAR-NK cell therapy targeting CD7 has emerged as a promising approach for treating T-cell malignancies. However, conventional CAR-NK cell therapy faces the challenges of cell fratricide due to CD7 expression on both malignant cells and normal NK cells. Additionally, engineering CARs into human tissue-derived NK cells demonstrates heterogeneity, low transduction efficiency, and high manufacturing costs.
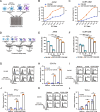
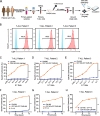
Methods: The human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) were genetically modified by knocking out the CD7 gene and introducing the CD7 CAR expression cassette to generate CD7 KO-CD7 CAR-hPSCs. These modified hPSCs were subsequently differentiated into CD7 KO-CD7 CAR-iNK cells using an efficient organoid induction method. The cytotoxicity of CD7 KO-CD7 CAR-iNK cells against CD7+ tumor cells was evaluated. Furthermore, we overexpressed the CXCR4 gene in CD7 KO-CD7 CAR-hPSCs and derived CXCR4-expressing CD7 KO-CD7 CAR-iNK (CRO-CD7 CAR-iNK) cells. The dynamics of CRO-CD7 CAR-iNK cells in vivo were tracked, and their therapeutic efficacy was assessed using human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) xenograft models.
Results: The CD7 KO-CD7 CAR-iNK cells derived from CD7 KO-CD7 CAR-hPSCs effectively avoided fratricide, demonstrated normal expansion, and exhibited potent and specific anti-tumor activity against CD7+ T-cell tumor cell lines and primary T-ALL cells. CXCR4 overexpression in CRO-CD7 CAR-iNK cells improved their homing capacity and extended their persistence in vivo. The CRO-CD7 CAR-iNK cells significantly suppressed tumor growth and prolonged the survival of T-ALL tumor-bearing mice.
Conclusions: Our study provides a reliable strategy for the large-scale generation of fratricide-resistant CD7 CAR-iNK cells with robust anti-tumor effects from hPSCs, offering a promising cell product to treat T-cell malignancies.
Keywords: CD7 CAR-NK; CXCR4; Fratricide-resistance; Human pluripotent stem cells; Persistence; T-ALL.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Experiments and handling of mice were conducted under the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The studies involving humans were approved by the Biomedical Research Ethics Committee of the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The use of patient samples was conducted in accordance with the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki. All patient samples were collected with priori patient consent signatures and were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology, Institute of Hematology and Blood Disease Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CD7-edited T cells expressing a CD7-specific CAR for the therapy of T-cell malignancies.Blood. 2017 Jul 20;130(3):285-296. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-01-761320. Epub 2017 May 24. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28539325 Free PMC article.
-
Inserting EF1α-driven CD7-specific CAR at CD7 locus reduces fratricide and enhances tumor rejection.Leukemia. 2023 Aug;37(8):1660-1670. doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-01948-3. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Leukemia. 2023. PMID: 37391486
-
CD7-deleted hematopoietic stem cells can restore immunity after CAR T cell therapy.JCI Insight. 2021 Aug 23;6(16):e149819. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.149819. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34423790 Free PMC article.
-
CAR-NK cell in cancer immunotherapy; A promising frontier.Cancer Sci. 2021 Sep;112(9):3427-3436. doi: 10.1111/cas.14993. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 34050690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CAR-NK Cells: From Natural Basis to Design for Kill.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 14;12:707542. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.707542. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34970253 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
G4SNVHunter: An R/Bioconductor Package for Evaluating SNV-Induced Disruption of G-Quadruplex Structures Leveraging the G4Hunter Algorithm.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 Aug 18;21(8):e1013368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1013368. eCollection 2025 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 40825076 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

