Nose-to-brain drug delivery: from bench to bedside
- PMID: 40390100
- PMCID: PMC12090632
- DOI: 10.1186/s40035-025-00481-w
Nose-to-brain drug delivery: from bench to bedside
Abstract
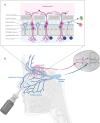
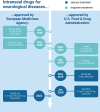
There is increasing interest in nose-to-brain delivery as an innovative drug delivery strategy for neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's or Alzheimer's disease. The unique anatomy of the nose-brain interface facilitates direct drug transport via the olfactory and trigeminal pathways to the brain, bypassing the blood-brain barrier. Different administration techniques as well as advanced drug formulations like targeted nanoparticles and thermoresponsive systems have been explored to improve the delivery efficiency and the therapeutic efficacy. This review provides an up-to-date perspective on this fast-developing field, and discusses different studies on safety and pharmacokinetic properties. A thorough evaluation of preclinical and clinical studies reveals both promises and challenges of this delivery method, highlighting approved drugs for the treatment of epilepsy and migraine that successfully utilize intranasal routes. The current landscape of research on nose-to-brain delivery is critically discussed, and a rationale is provided for ongoing research to optimize therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Alzheimer's; Intranasal; N2B; Nanoparticle; Neurodegenerative disease; Parkinson's.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Convolutions in the rendition of nose to brain therapeutics from bench to bedside: Feats & fallacies.J Control Release. 2022 Jan;341:782-811. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.12.009. Epub 2021 Dec 11. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 34906605 Review.
-
Lipid nanoparticles for intranasal administration: application to nose-to-brain delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2018 Apr;15(4):369-378. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2018.1429401. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 29338427 Review.
-
Intranasal nanoparticulate delivery systems for neurodegenerative disorders: a review.Ther Deliv. 2023 Sep;14(9):571-594. doi: 10.4155/tde-2023-0019. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Ther Deliv. 2023. PMID: 37691577 Review.
-
Insights into direct nose to brain delivery: current status and future perspective.Drug Deliv. 2014 Mar;21(2):75-86. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2013.838713. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 24102636 Review.
-
Intranasal delivery bypasses the blood-brain barrier to target therapeutic agents to the central nervous system and treat neurodegenerative disease.BMC Neurosci. 2008 Dec 10;9 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-S3-S5. BMC Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19091002 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of current situation of psychotropic drugs research and development in China based on drug clinical trials.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 15;16:1599038. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1599038. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40735218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kiran P, Debnath SK, Neekhra S, Pawar V, Khan A, Dias F, et al. Designing nanoformulation for the nose-to-brain delivery in Parkinson’s disease: advancements and barrier. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022;14(1):e1768. - PubMed
-
- Dahl R, Mygind N. Anatomy, physiology and function of the nasal cavities in health and disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1998;29(1–2):3–12. - PubMed
-
- Pires A, Fortuna A, Alves G, Falcão A. Intranasal drug delivery: how, why and what for? J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2009;12(3):288–311. - PubMed
-
- Schuenke M, Schulte E, Schumacher U, Ross LM, Lamperti ED, Taub E, editors. Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: Head and Neuroanatomy. Stuttgart, Germany: Thieme; 2010.
-
- Sasaki K, Fukakusa S, Torikai Y, Suzuki C, Sonohata I, Kawahata T, et al. Effective nose-to-brain drug delivery using a combination system targeting the olfactory region in monkeys. J Control Release. 2023;359:384–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

