Health inequalities in disease burden of dementia and early-onset dementia: findings from the Global Burden of Disease 2021 study
- PMID: 40390116
- PMCID: PMC12087054
- DOI: 10.1186/s41256-025-00417-x
Health inequalities in disease burden of dementia and early-onset dementia: findings from the Global Burden of Disease 2021 study
Abstract
Background: Given the increasing aging global population and advancements in dementia action plans, the latest disparities in the dementia burden may evolve. This study aimed to analyze and compare temporal trends at regional, national, and sociodemographic levels to provide evidence for public health planning and resource prioritization.
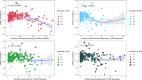
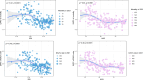
Methods: The age-standardized prevalence rate (ASPR), age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR), age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR), and age-standardized disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) rate (ASDR) were derived from the Global Burden of Disease 2021 study. Estimated annual percentage changes (EAPCs) were calculated to quantify their temporal trends. Correlations between EAPC and the human resources for health (HRH) were assessed using Pearson correlation analysis.
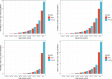
Results: Although the ASPR and ASIR remained stable or decreased globally, they both greatly increased in East Asia (ASPR: EAPC = 0.43; 95% CI 0.35, 0.51; ASIR: EAPC = 0.40; 95% CI 0.33, 0.47). For early-onset dementia, the ASPR (range of EAPC = 0.03-0.17) and ASIR (range of EAPC = 0.05-0.19) in the 45 to 59 years age group increased in North Africa and Middle East, particularly among females (ASPR: range of EAPC = 0.08-0.21; ASIR: range of EAPC = 0.09-0.2). Although the ASMR and ASDR both decreased globally and in high socio-demographic index region, they both increased greatly in South Asia (ASMR: EAPC = 0.7; 95% CI 0.66, 0.75; ASDR: EAPC = 0.40; 95% CI 0.37, 0.43). For early-onset dementia, the ASMR (range of EAPC = 0.43-0.78) and ASDR (range of EAPC = 0.19-0.33) in the 40 to 59 years age group had increased in Central Sub-Saharan Africa, particularly among females (ASMR: range of EAPC = 0.5-0.86; ASDR: range of EAPC = 0.19-0.4). Negative correlations were observed between the EAPC in ASPR, ASIR, ASMR and ASDR with various types of HRH at the national level.
Conclusions: Although there has been progresses in controlling the global trends of dementia incidence, prevalence, and mortality, significant regional and national inequalities remain evident. More importantly, the early-onset dementia burden is increasing significantly among females in the African region, underscoring the critical need for healthcare systems that address dementia across the early midlife span.
Keywords: Dementia; Early-onset; Health disparities; Incidence; Mortality.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: For GBD studies, the Institutional Review Board of the University of Washington reviewed and approved a waiver of informed consent. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Global, regional, and national burden of gastritis and duodenitis from 1990 to 2021 with projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Int J Med Sci. 2025 May 10;22(11):2570-2582. doi: 10.7150/ijms.109762. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40520897 Free PMC article.
-
The global, regional, and national burden of paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction, 1990 to 2021: a cross-sectional analysis from the 2021 global burden of disease study.Int J Surg. 2025 Feb 1;111(2):1773-1787. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002189. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39784557
-
Burden of uterine cancer in China from 1990 to 2021 and 15-year projection: a systematic analysis and comparison with global levels.Reprod Health. 2024 Oct 10;21(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12978-024-01882-2. Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 39390595 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden, risk factors, and projections of early-onset dementia: Insights from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Feb;104:102644. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102644. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39701185 Review.
-
Evolving landscape of colorectal cancer: Global and regional burden, risk factor dynamics, and future scenarios (the Global Burden of Disease 1990-2050).Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Feb;104:102666. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2025.102666. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39828028 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Dementia. 2023. https://www.who.int/health-topics/dementia#tab=tab_1[20250105]
-
- Global action plan on the public health response to dementia 2017–2025. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
-
- Long S, Benoist C, Weidner W. World Alzheimer Report 2023: Reducing dementia risk: never too early, never too late. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International; 2023.
-
- Global status report on the public health response to dementia: executive summary. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

