hiPSC-neurons recapitulate the subtype-specific cell intrinsic nature of susceptibility to neurodegenerative disease-relevant aggregation
- PMID: 40390134
- PMCID: PMC12087151
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-025-02000-4
hiPSC-neurons recapitulate the subtype-specific cell intrinsic nature of susceptibility to neurodegenerative disease-relevant aggregation
Abstract
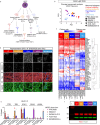
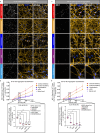
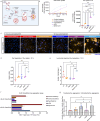
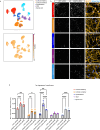
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by the accumulation and spread of Tau intraneuronal inclusions throughout most of the telencephalon, leaving hindbrain regions like the cerebellum and spinal cord largely spared. These neuropathological observations, along with the identification of specific vulnerable sub-populations from AD brain-derived single nuclei transcriptomics, suggest that a subset of brain regions and neuronal subtypes possess a selective vulnerability to Tau pathology. Given the inability to culture neurons from patient brains, a disease-relevant in vitro model which recapitulates these features would serve as a critical tool to validate modulators of vulnerability and resilience. Using our recently established platform for inducing endogenous Tau aggregation in human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived cortical excitatory neurons via application of AD brain-derived exogenous Tau aggregates, we explored whether Tau aggregates preferentially induce aggregation in specific neuronal subtypes. We compared Tau seeding in hiPSC-derived neuron subtypes representing regional identities across the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Higher susceptibility (i.e. more Tau aggregation) was consistently observed among cortical neuron subtypes, with CTIP2-positive, somatostatin (SST)-positive cortical inhibitory neurons showing the greatest aggregation levels across hiPSC lines from multiple donors. hiPSC-neurons also delineated between the disease-specific vulnerabilities of different protein aggregates, as α-synuclein preformed fibrils showed an increased propensity to induce aggregates in midbrain dopaminergic (mDA)-like neurons, mimicking Parkinson's disease (PD)-specific susceptibility. Aggregate uptake and degradation rates were insufficient to explain differential susceptibility. The absence of a consistent transcriptional response following aggregate seeding further indicated that intrinsic neuronal subtype-specific properties could drive susceptibility. The present data provides evidence that hiPSC-neurons exhibit features of selective neuronal vulnerability which manifest in a cell autonomous manner, suggesting that mining intrinsic (or basal) transcriptomic signatures of more vulnerable compared to more resilient hiPSC-neurons could uncover the molecular underpinnings of differential susceptibility to protein aggregation found in a variety of neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; Selective vulnerability; Tau; hiPSC-derived neurons.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Written informed consent for primary tissue procurement and the use of the material and clinical information for research purposes was obtained by the brain banks and the hiPSC providers (commercial sources or consortiums) used in this study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: Funding/Competing interests C.N.P., S.E.C., L.G., G.L., M.S.B., J.L., L.M.R., O.M., K.N.N., N.R.P., Q.L., P.R., R.W., D.E.E., A.S., S.B., C.X., B.S., M.C., N.R., K.Y., A.M.W., J.W., L.G., J.S., X.L., and J.D.M are employees of AbbVie. I.W., G.S. T.J.K, and M.W. were employees at the time of the study. The design, study conduct, and financial support for this research were provided by AbbVie. AbbVie participated in the interpretation of data, review, and approval of the publication.
Figures

References
-
- Aleksander SA, Balhoff J, Carbon S, Cherry JM, Drabkin HJ, Ebert D, Feuermann M, Gaudet P, Harris NL, Hill DP, Lee R, Mi H, Moxon S, Mungall CJ, Muruganugan A, Mushayahama T, Sternberg PW, Thomas PD, Auken KV, Ramsey J, Siegele DA, Chisholm RL, Fey P, Aspromonte MC, Nugnes MV, Quaglia F, Tosatto S, Giglio M, Nadendla S, Antonazzo G, Attrill H, dos Santos G, Marygold S, Strelets V, Tabone CJ, Thurmond J, Zhou P, Ahmed SH, Asanitthong P, Buitrago DL, Erdol MN, Gage MC, Kadhum MA, Li KYC, Long M, Michalak A, Pesala A, Pritazahra A, Saverimuttu SCC, Su R, Thurlow KE, Lovering RC, Logie C, Oliferenko S, Blake J, Christie K, Corbani L, Dolan ME, Drabkin HJ, Hill DP, Ni L, Sitnikov D, Smith C, Cuzick A, Seager J, Cooper L, Elser J, Jaiswal P, Gupta P, Jaiswal P, Naithani S, Lera-Ramirez M, Rutherford K, Wood V, Pons JLD, Dwinell MR, Hayman GT, Kaldunski ML, Kwitek AE, Laulederkind SJF, Tutaj MA, Vedi M, Wang S-J, D’Eustachio P, Aimo L, Axelsen K, Bridge A, Hyka-Nouspikel N, Morgat A, Aleksander SA, Cherry JM, Engel SR, Karra K, Miyasato SR, Nash RS, Skrzypek MS, Weng S, Wong ED, Bakker E, Berardini TZ, Reiser L, Auchincloss A, Axelsen K, Argoud-Puy G, Blatter M-C, Boutet E, Breuza L, Bridge A, Casals-Casas C, Coudert E, Estreicher A, Famiglietti ML, Feuermann M, Gos A, Gruaz-Gumowski N, Hulo C, Hyka-Nouspikel N, Jungo F, Mercier PL, Lieberherr D, Masson P, Morgat A, Pedruzzi I, Pourcel L, Poux S, Rivoire C, Sundaram S, Bateman A, Bowler-Barnett E, Bye-A-Jee H, Denny P, Ignatchenko A, Ishtiaq R, Lock A, Lussi Y, Magrane M, Martin MJ, Orchard S, Raposo P, Speretta E, Tyagi N, Warner K, Zaru R, Diehl AD, Lee R, Chan J, Diamantakis S, Raciti D, Zarowiecki M, Fisher M, James-Zorn C, Ponferrada V, Zorn A, Ramachandran S, Ruzicka L, Westerfield M, Aleksander SA, Balhoff J, Carbon S, Cherry JM, Drabkin HJ, Ebert D, Feuermann M, Gaudet P, Harris NL, Hill DP, Lee R, Mi H, Moxon S, Mungall CJ, Muruganugan A, Mushayahama T, Sternberg PW, Thomas PD, Auken KV, Ramsey J, Siegele DA, Chisholm RL, Fey P, Aspromonte MC, Nugnes MV, Quaglia F, Tosatto S, Giglio M, Nadendla S, Antonazzo G, Attrill H, dos Santos G, Marygold S, Strelets V, Tabone CJ, Thurmond J, Zhou P, Ahmed SH, Asanitthong P, Buitrago DL, Erdol MN, Gage MC, Kadhum MA, Li KYC, Long M, Michalak A, Pesala A, Pritazahra A, Saverimuttu SCC, Su R, Thurlow KE, Lovering RC, Logie C, Oliferenko S, Blake J, Christie K, Corbani L, Dolan ME, Drabkin HJ, Hill DP, Ni L, Sitnikov D, Smith C, Cuzick A, Seager J, Cooper L, Elser J, Jaiswal P, Gupta P, Jaiswal P, Naithani S, Lera-Ramirez M, Rutherford K, Wood V, Pons JLD, Dwinell MR, Hayman GT, Kaldunski ML, Kwitek AE, Laulederkind SJF, Tutaj MA, Vedi M, Wang S-J, D’Eustachio P, Aimo L, Axelsen K, Bridge A, Hyka-Nouspikel N, Morgat A, Aleksander SA, Cherry JM, Engel SR, Karra K, Miyasato SR, Nash RS, Skrzypek MS, Weng S, Wong ED, Bakker E, Berardini TZ, Reiser L, Auchincloss A, Axelsen K, Argoud-Puy G, Blatter M-C, Boutet E, Breuza L, Bridge A, Casals-Casas C, Coudert E, Estreicher A, Famiglietti ML, Feuermann M, Gos A, Gruaz-Gumowski N, Hulo C, Hyka-Nouspikel N, Jungo F, Mercier PL, Lieberherr D, Masson P, Morgat A, Pedruzzi I, Pourcel L, Poux S, Rivoire C, Sundaram S, Bateman A, Bowler-Barnett E, Bye-A-Jee H, Denny P, Ignatchenko A, Ishtiaq R, Lock A, Lussi Y, Magrane M, Martin MJ, Orchard S, Raposo P, Speretta E, Tyagi N, Warner K, Zaru R, Diehl AD, Lee R, Chan J, Diamantakis S, Raciti D, Zarowiecki M, Fisher M, James-Zorn C, Ponferrada V, Zorn A, Ramachandran S, Ruzicka L, Westerfield M (2023) The Gene ontology knowledgebase in 2023. Genetics 224:iyad031. 10.1093/genetics/iyad031 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G (2000) Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25:25–29. 10.1038/75556 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barini E, Plotzky G, Mordashova Y, Hoppe J, Rodriguez-Correa E, Julier S, LePrieult F, Mairhofer I, Mezler M, Biesinger S, Cik M, Meinhardt MW, Ercan-Herbst E, Ehrnhoefer DE, Striebinger A, Bodie K, Klein C, Gasparini L, Schlegel K (2022) Tau in the brain interstitial fluid is fragmented and seeding–competent. Neurobiol Aging 109:64–77. 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.09.013 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bichmann M, Oriol NP, Ercan-Herbst E, Schöndorf DC, Ramos BG, Schwärzler V, Neu M, Schlüter A, Wang X, Jin L, Hu C, Tian Y, Ried JS, Haberkant P, Gasparini L, Ehrnhoefer DE (2021) SETD7-mediated monomethylation is enriched on soluble Tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 16:46. 10.1186/s13024-021-00468-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blum H, Beier H, Gross HJ (1987) Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 8:93–99. 10.1002/elps.1150080203 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

