TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 4: A phase 3 trial comparing donanemab with aducanumab on amyloid plaque clearance in early, symptomatic Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40390253
- PMCID: PMC12089073
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70293
TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 4: A phase 3 trial comparing donanemab with aducanumab on amyloid plaque clearance in early, symptomatic Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: The phase 3, open-label TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 4 study compared the effect of donanemab versus aducanumab on amyloid plaque (AP) clearance in participants with early symptomatic Alzheimer's disease.
Methods: Participants (n = 148) were randomized 1:1 to receive intravenous donanemab (700 mg every 4 weeks for three doses, then 1400 mg every 4 weeks thereafter) or aducanumab (per label). AP was measured with florbetapir F 18 positron emission tomography. AP clearance was defined as < 24.1 Centiloids.
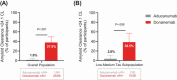
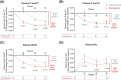
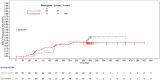
Results: At 6, 12, and 18 months, AP clearance was achieved in 37.9%, 70.0%, and 76.8%, respectively, of donanemab-treated participants versus 1.6%, 24.6%, and 43.1% of aducanumab-treated participants (P < 0.001). Median time to clearance was 359 versus 568 days for donanemab- versus aducanumab-treated participants (P < 0.001). Amyloid-related imaging abnormality (ARIA)-edema/effusion occurred in 23.9% and 34.8% of donanemab- and aducanumab-treated participants, respectively.
Discussion: Donanemab treatment resulted in earlier and greater AP clearance compared to aducanumab. ARIA frequencies were consistent with prior studies.
Clinical trial registration: No: NCT05108922, TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 4 HIGHLIGHTS: Here we report the first direct comparator study of two amyloid-targeting therapies. This was the first investigation of donanemab on biomarker efficacy regardless of tau levels. Donanemab demonstrated superiority over aducanumab in amyloid plaque (AP) clearance. The depth and speed of AP removal did not affect amyloid-related imaging abnormality risk or incidence.
Keywords: aducanumab; amyloid clearance; amyloid‐related imaging abnormalities; amyloid‐targeting therapies; donanemab; infusion‐related reaction.
© 2025 Eli Lilly and Company. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Stephen Salloway: Butler Hospital receives research support for conducting clinical trials through grants or contracts from Biogen, Eisai, Genentech, Roche, CognitionRx, Eli Lilly and Company, and Janssen. He has received consulting fees from Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Biogen, Biohaven, Cognition, Eisai, Fujirebio, Genentech, Kisbee, Laqbcorp, Lilly, Merck, Neurophet, NovoNordisk, Prothena, Quest, and Roche. Dr. Salloway is an author for the Appropriate Use Recommendations for aducanumab, lecanemab, and donanemab. Elly Lee: Irvine Clinical research receives study‐related funds from Eli and Company, Eisai, Biogen, Prothena, Abbvie, BMS, Janssen, Acumen, Roche, and Neumora. Michelle Papka received consulting fees from Eli Lilly and Company. Andrew Pain, Margaret B. Ferguson, Hong Wang, Haoyan Hu, Ming Lu, Ena Oru, Paul A. Ardayfio, Deirdre B. Hoban, Emily C. Collins, Dawn A. Brooks, and John R. Sims are employees of and minor shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

