Liver as a nexus of daily metabolic cross talk
- PMID: 40390465
- PMCID: PMC12092977
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2024.06.001
Liver as a nexus of daily metabolic cross talk
Abstract
Over the course of a day, the circadian clock promotes a homeostatic balance between energy intake and energy expenditure by aligning metabolism with nutrient availability. In mammals, this process is driven by central clocks in the brain that control feeding behavior, the peripheral nervous system, and humoral outputs, as well as by peripheral clocks in non-brain tissues that regulate gene expression locally. Circadian organization of metabolism is critical, as circadian disruption is associated with increased risk of metabolic disease. Emerging evidence shows that circadian metabolism hinges upon inter-organ cross talk involving the liver, a metabolic hub that integrates many facets of systemic energy homeostasis. Here, we review spatiotemporal interactions, mainly metabolite exchange, signaling factors, and hormonal control, between the liver and skeletal muscle, pancreas, gut, microbiome, and adipose tissue. Modern society presents the challenge of circadian disturbances from rotating shift work to social jet lag and 24/7 food availability. Thus, it is important to better understand the mechanisms by which the clock system controls metabolic homeostasis and work toward targeted therapies.
Keywords: Circadian clock; Circadian rhythm; Hepatic metabolism; Inter-organ cross talk; Liver; Molecular clock; Systems biology.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
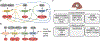
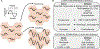

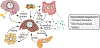
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

