Knowledge of HIV status among mothers accompanying their infants for immunization in Machakos, Kenya, 2014
- PMID: 40390790
- PMCID: PMC12087675
- DOI: 10.58498/eajahme.v4i4.27
Knowledge of HIV status among mothers accompanying their infants for immunization in Machakos, Kenya, 2014
Abstract
Background: Elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV is achievable through prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) interventions. For HIV-positive mothers to access PMTCT services, they must be identified through HIV testing and counseling. We sought to measure the proportion of mothers with unknown HIV status and to determine associated factors.
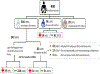
Methods: We recruited into a cross-sectional study 400 mothers accompanying their infants for routine immunization at mother-child health clinic (MCH) at Machakos Hospital, Kenya, collected information on HIV testing from their antenatal records, and offered opt-out HIV testing to those with unknown HIV status.
Results: Overall, 304 (76.0%) mothers had unknown status at MCH, of whom 25 (8.6%) tested HIV-positive. HIV positivity was three times higher among mothers who never tested during pregnancy/delivery versus those whose last negative HIV test was >3 months prior to study enrolment (18% versus 6%). Women living more than three kilometers away from the health facility had 2.7-fold greater odds of having unknown status compared to those who lived less than three kilometers (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] 2.7, 95% CI 1.3-5.6). Married women had 3.2-fold greater odds of having unknown status as compared to those who were single (AOR 3.2, 95% CI 1.4-7.0). Those with education had a tenfold reduction in odds of having unknown status compared to those with none (AOR 0.1, 95% CI 0.0-0.2).
Conclusion: Interventions are needed to improve women's ANC attendance, uptake of HIV testing, and disclosure of HIV status during pregnancy to achieve the elimination of MTCT.
Keywords: HIV; MCH; PMTCT; Unknown HIV status.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and correlates of non-disclosure of maternal HIV status to male partners: a national survey in Kenya.BMC Public Health. 2018 May 30;18(1):671. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5567-6. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29848345 Free PMC article.
-
Mother-baby dyads enrolled in PMTCT care in western Kenya: characteristics and implications for ART programmes.Afr J AIDS Res. 2018 Sep;17(3):241-247. doi: 10.2989/16085906.2018.1508044. Epub 2018 Oct 14. Afr J AIDS Res. 2018. PMID: 30319032
-
Male partner involvement in the prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV infection in Mwanza Region, Tanzania.Pan Afr Med J. 2017 Jun 6;27:90. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2017.27.90.8901. eCollection 2017. Pan Afr Med J. 2017. PMID: 28819511 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the uptake and determinants of prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV services in East Africa: Mixed methods systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 18;19(4):e0300606. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300606. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38635647 Free PMC article.
-
Non-booking for antenatal care and risks for vertical HIV transmission among women in Chitungwiza, Zimbabwe: a cross-sectional study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022 Nov 5;22(1):817. doi: 10.1186/s12884-022-05131-x. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022. PMID: 36335299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asweto CO, Aluoch JR, Obonyo CO, & Ouma JO (2014). Maternal Autonomy, Distance to Health Care Facility and ANC Attendance: Findings from Madiany Division of Siaya County, Kenya. 2(4), 153–158. 10.12691/ajphr-2-4-5 - DOI
-
- Hanson C, Cox J, Mbaruku G, Manzi F, Gabrysch S, Schellenberg D, … Foundation, M. G. (2015). Maternal mortality and distance to facility-based obstetric care in rural southern Tanzania: a secondary analysis of cross-sectional census data in 226 000 households. The Lancet Global Health, 3(7), e387–e395. 10.1016/S2214-109X(15)00048-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). (2012). Global report: UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources