Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- PMID: 40391080
- PMCID: PMC12086630
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2025-1194
Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: Dioscin (Dio) is an important anti-tumor active component found in the seeds of Livistona chinensis. However, the efficacy and mechanism of Dio in relation to the progression of glioblastoma (GBM) remain unclear.
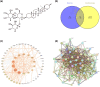
Materials and methods: Using 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide assays, flow cytometry, and Hoechst staining in vitro experiments. A tumor-bearing nude mouse model was employed to further explore the impact of Dio on GBM tumor growth in vivo experiments. Using network pharmacological analysis and molecular docking to predict the potential target proteins and signaling pathways of Dio anti-GBM. The expression of proteins associated with apoptotic pathways was assessed by western blotting.
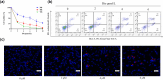
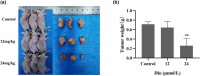
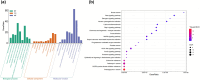
Results: Dio effectively suppresses the proliferation and promotes apoptosis of U251 cells. In the established tumor-bearing nude mouse model, the anti-cancer activity of Dio was further assessed. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis highlighted cancer signaling pathways, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Western blot results showed that EGFR phosphorylation and apoptosis gene CASP3 increased with the increase of Dio concentration.
Conclusions: Dio could inhibit the proliferation and promote apoptosis of GBM cells, and play a significant inhibitory role in tumor growth. Dio could affect the phosphorylation of EGFR and then trigger the apoptosis process, resulting in the up-regulation of apoptosis protein CASP3 expression in GBM cells.
Keywords: Dioscin; EGFR; apoptotic pathway; glioblastoma; network pharmacology.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dioscin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth by inducing apoptosis and regulation of TP53, BAX, BCL2 and cleaved CASP3.Phytomedicine. 2016 Nov 15;23(12):1329-1336. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27765352
-
Exploring the therapeutic mechanisms and prognostic targets of Biochanin A in glioblastoma via integrated computational analysis and in vitro experiments.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 15;14(1):3783. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53442-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38360888 Free PMC article.
-
A network pharmacology approach and experimental validation to investigate the anticancer mechanism and potential active targets of ethanol extract of Wei-Tong-Xin against colorectal cancer through induction of apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;303:115933. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115933. Epub 2022 Nov 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36403742
-
Muscone restores anoikis sensitivity in TMZ-resistant glioblastoma cells by suppressing TOP2A via the EGFR/Integrin β1/FAK signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul;129:155714. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155714. Epub 2024 May 5. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38723526
-
Enhancing temozolomide efficacy in GBM: The synergistic role of chuanxiong rhizoma essential oil.Phytomedicine. 2025 May;140:156575. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156575. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40088740
References
-
- Tao X, Yin L, Xu L, Peng J. Dioscin: a diverse acting natural compound with therapeutic potential in metabolic diseases, cancer, inflammation and infections. Pharmacol Res. 2018;137:259–69. - PubMed
-
- Xi P, Niu Y, Zhang Y, Li W, Gao F, Gu W, et al. The mechanism of dioscin preventing lung cancer based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;292:115138. - PubMed
-
- Li R, Qin J, Wang Z, Lv F, Guo J, Zhu H, et al. Dioscin reduced chemoresistance for colon cancer and analysis of sensitizing targets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;638:94–102. - PubMed
-
- Ma T, Ge X, Zhu J, Song C, Wang P, Cai J. Dioscin impedes proliferation, metastasis and enhances autophagy of gastric cancer cells via regulating the USP8/TGM2 pathway. Mol Biotechnol. 2024;66(12):3700–11. - PubMed
-
- Ding Q, Zhang W, Cheng C, Mo F, Chen L, Peng G, et al. Dioscin inhibits the growth of human osteosarcoma by inducing G2/M-phase arrest, apoptosis, and GSDME-dependent cell death in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(3):2911–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
