Aptamers: Design, Theory, and Applications to Diagnosis and Therapy for Diseases
- PMID: 40391083
- PMCID: PMC12086380
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70180
Aptamers: Design, Theory, and Applications to Diagnosis and Therapy for Diseases
Abstract
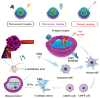
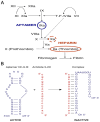
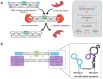
Single-stranded DNA or RNA entities referred to as aptamers exhibit a strong affinity and specificity for attaching to specific targets. Owing to their special properties, which include simplicity of synthesis, low immunogenicity, and adaptability in targeting a variety of substances, these synthetic oligonucleotides have garnered a lot of interest. The function of aptamers can be altered by combining them with complementary oligonucleotides "antidotes," which are antisense to a particular aptamer sequence. Antidotes play an important role in several fields by specifically targeting the corresponding section of the aptamer. Nevertheless, even with their promising capabilities, the creation of antidotes to regulate or inhibit aptamer function continues to be a relatively unexamined field, constraining their secure and efficient application in medical environments. The review explores experimental methodologies for creating antidotes, the systematic design strategies for managing antidotes in aptamer-based therapies, and their therapeutic efficacy in counteracting disease biomarkers. Additionally, it highlights their diagnostic applications in biosensing and imaging, offering a promising alternative to traditional antibodies. It also investigates the progress, latest innovations, and potential medical uses of aptamer-antidote combinations. Its academic value lies in bridging the gap between theoretical design and practical applications, providing researchers and clinicians with a comprehensive resource to advance aptamer-based solutions in medicine and biotechnology.
Keywords: antidote; aptamer; reversible therapeutics.
© 2025 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An overview of aptamer: Design strategy, prominent applications, and potential challenge in plants.J Plant Physiol. 2024 May;296:154235. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2024.154235. Epub 2024 Mar 19. J Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38531181 Review.
-
Rapid Complexation of Aptamers by Their Specific Antidotes.Molecules. 2017 Jun 8;22(6):954. doi: 10.3390/molecules22060954. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28594360 Free PMC article.
-
Antidote control of aptamer therapeutics: the road to a safer class of drug agents.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012 Aug;13(10):1924-34. doi: 10.2174/138920112802273137. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22352726 Review.
-
Reversible Aptamer Staining, Sorting, and Cleaning of Cells (Clean FACS) with Antidote Oligonucleotide or Nuclease Yields Fully Responsive Cells.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2024 Feb;34(1):12-17. doi: 10.1089/nat.2023.0050. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2024. PMID: 38285522 Free PMC article.
-
Development of universal antidotes to control aptamer activity.Nat Med. 2009 Oct;15(10):1224-8. doi: 10.1038/nm.1990. Epub 2009 Oct 4. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19801990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xie J., Wang Y., Choi W., et al., “Overcoming Barriers in Photodynamic Therapy Harnessing Nano‐formulation Strategies,” Chemical Society Reviews 50, no. 16 (2021): 9152–9201. - PubMed
-
- Didarian R., Ozbek H. K., Ozalp V. C., Erel O., and Yildirim‐Tirgil N., “Enhanced SELEX Platforms for Aptamer Selection With Improved Characteristics: A Review,” Molecular Biotechnology (2024): 1–16. - PubMed
-
- Jain N., Singh A., and Bhatia D., “DNA‐amphiphilic Nanostructures: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications,” Nanoscale 17 (2025): 18–52. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
