Yi-Fei-Tong-Bi Decoction Alleviates Bleomycin Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice
- PMID: 40391179
- PMCID: PMC12087589
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S515368
Yi-Fei-Tong-Bi Decoction Alleviates Bleomycin Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice
Abstract
Background: Fei-Bi decoction, a Chinese ancient experience decoction collected in the book of Bianzhenglu (Syndrome Differentiation Record). Based on Fei-Bi Decoction, Yi-Fei-Tong-Bi decoction (YFTBD) is developed and has a significant effect in the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis. However, the underlying mechanisms of YFTBD affects pulmonary fibrosis remain to be elucidated.
Purpose: To investigate the protective effect and the underlying mechanism of YFTBD on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.
Methods: The chemical components of water extract of YFTBD were analyzed by combining the high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with mass spectrometry (MS). A mouse model was established by intratracheal injection of bleomycin, and the effects of YFTBD were evaluated through pathological staining, immunohistochemistry analyses, and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Subsequently, the effect of YFTBD on the gut microbiota of mice was analyzed by 16S rRNA high-throughput gene sequencing.
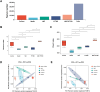
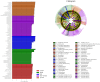
Results: Compared with the model group, the survival rate and lung coefficient of mice with pulmonary fibrosis were increased after the intervention of YFTBD, the pathological morphology of lung tissue was improved, and the expression of the inflammatory factor levels were decreased. The expression of α-SMA, TGF-β1, p21, and p16 senescence-related proteins was significantly down-regulated. The expression of Smad7 and PGC-1α senescence-related proteins was significantly up-regulated. Meanwhile, gut microbiota analysis showed that YFTBD could induce changes in the abundance of Alloprevotella, unclassified Muribaculaceae, and Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that YFTBD could alleviate the bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice via regulating TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway, inflammation and gut microbiota. It provides experimental evidence and a theoretical basis for the application of YFTBD in pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: Yi-Fei-Tong-Bi decoction; cell senescence; collagen; gut microbiota; pulmonary fibrosis.
© 2025 Du et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




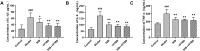

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

