In Vitro Validation of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) as an Effective Countermeasure Against Inflammatory-Mediated Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
- PMID: 40391205
- PMCID: PMC12086804
- DOI: 10.1002/jsp2.70077
In Vitro Validation of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) as an Effective Countermeasure Against Inflammatory-Mediated Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
Abstract
Background: Intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration (IDD) is the main contributor to chronic low back pain (LBP), the leading cause of disability worldwide, with a significant impact on the quality of life and health of common people. The etiology of IDD is still unclear, but it has been largely demonstrated the crucial role of inflammation and neuroinflammation in the pathological and degenerative cascade of events characterizing IVD degeneration.
Aim: In this study, we evaluated the potential therapeutic effect of pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) on human degenerated IVD (D-IVD) cells collected from patients who underwent discectomy.
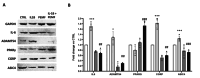
Materials & methods: The experimental plan to test our hypothesis, involved viability assay, reactive oxide species/nitrite production, gene, and protein expression. To recapitulate the pro-inflammatory disc microenvironment occurring during IDD, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) was administered to IVD cell culture. Then, to dissect the contribution of neuroinflammatory condition to immune component, microglial cells were co-cultured with IVD-conditioned media, and viability and expression of inflammatory markers were detected.
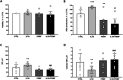
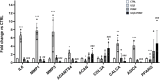
Results: Our data prove that in the IVD degenerative microenvironment, the increase of pro-inflammatory mediators, extracellular matrix degradative enzymes, and neuroinflammatory markers could be reduced by PEMF therapy, resulting in an overall improvement of degenerative condition and LBP.
Conclusion: These results represent an impactful novelty for the management of people suffering from LPB, in terms of symptom relief and reduction of social-health system burden.
Keywords: inflammation; intervertebral disc degeneration; microglia; pilots; pulsed electromagnetic field; space.
© 2025 The Author(s). JOR Spine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Orthopaedic Research Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Activating Sirt1-Autophagy Signaling Network.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 21;10:853872. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.853872. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35387300 Free PMC article.
-
Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) treatment reduces expression of genes associated with disc degeneration in human intervertebral disc cells.Spine J. 2016 Jun;16(6):770-6. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Spine J. 2016. PMID: 26780754
-
Mechanical loading of intervertebral disc modulates microglia proliferation, activation, and chemotaxis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018 Jul;26(7):978-987. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.04.013. Epub 2018 May 1. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018. PMID: 29723636
-
Gut-disc axis: A cause of intervertebral disc degeneration and low back pain?Eur Spine J. 2022 Apr;31(4):917-925. doi: 10.1007/s00586-022-07152-8. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Eur Spine J. 2022. PMID: 35286474 Review.
-
The mechanisms and functions of IL-1β in intervertebral disc degeneration.Exp Gerontol. 2023 Jun 15;177:112181. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2023.112181. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Exp Gerontol. 2023. PMID: 37088216 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

