Neutrophil extracellular traps in diseases of the female reproductive organs
- PMID: 40391215
- PMCID: PMC12086147
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1589329
Neutrophil extracellular traps in diseases of the female reproductive organs
Abstract
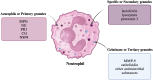
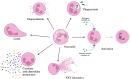
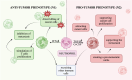
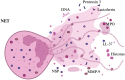
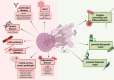
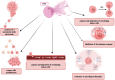
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are physiologically released in response to pathogens, serving as a defense mechanism. However, excessive NET production has been implicated in various pathological conditions, including diseases of the female reproductive system. Recent studies highlight the significant role of neutrophils and NETs in cancer pathogenesis. Overproduction of NETs creates sites for tumor cell adhesion, promoting tumor cell proliferation, immune escape, and tumor progression. NET formation is associated with many diseases, including cancers of the female reproductive organs. Detection of NETs can be used as a prognostic tool for patients with diseases characterized by higher rates of NETs formation, such as cancer. In order to use NETs in diagnosis, it is possible to determine them directly or to determine NET components: extracellular DNA, citrullinated histones, NE or MPO. This review explores the role of neutrophils and NETs in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of breast, ovarian, cervical and endometrial cancer, premature lapse of ovarian function, cervicitis, endometriosis, pregnancy and pregnancy-related diseases.
Keywords: NETs; breast cancer; gynecological cancer; gynecological diseases; neutrophils.
Copyright © 2025 Morawiec, Kubina, Stępień, Smycz-Kubańska, Królewska-Daszczyńska, Ratajczak-Wrona and Mielczarek-Palacz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps in tumor progression of gynecologic cancers.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 1;15:1421889. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1421889. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39555072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in stages, outcomes and pregnancy complications.J Reprod Immunol. 2024 Jun;163:104237. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2024.104237. Epub 2024 Mar 8. J Reprod Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38503075 Review.
-
Detection, Visualization, and Quantification of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) and NET Markers.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2087:425-442. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0154-9_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31729003
-
Enhanced Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Acute Pancreatitis Contributes to Disease Severity and Is Reduced by Chloroquine.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 24;10:28. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00028. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30733719 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote T Cell Exhaustion in the Tumor Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 24;12:785222. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.785222. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34899751 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

