CXCL1 and CXCL2: Key Regulators of Host Defense Against Phialophora verrucosa
- PMID: 40391231
- PMCID: PMC12087586
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S518653
CXCL1 and CXCL2: Key Regulators of Host Defense Against Phialophora verrucosa
Abstract
Purpose: Dematiaceous fungi, such as Phialophora verrucosa (P. verrucosa), cause persistent infections that are difficult to treat. The purpose of this study was to investigate the roles of chemokines CXCL1 and CXCL2 in the innate immune defense against P. verrucosa infections.
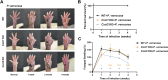
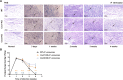
Methods: A subcutaneous infection model was employed, in which live P. verrucosa conidia were administered into the footpads of wild-type C57BL/6 mice and their Cxcl1 and Cxcl2 knockout (KO) counterparts (equal numbers of male and female mice). The natural course of infection, pathological changes, and immune responses were monitored continuously over four weeks.
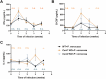
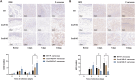
Results: The current results show that both CXCL1 and CXCL2 deficiencies impair fungal clearance, leading to prolonged infection as evidenced by higher fungal loads and histopathology in Cxcl1/Cxcl2 KO mice at week 4. In Cxcl1 KO mice, increased levels of inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ, G-CSF, and IL-4 were observed, likely compensating for the immunological deficiencies caused by the lack of CXCL1. Conversely, Cxcl2 KO mice exhibited impaired neutrophil infiltration early in infection, accompanied by a significant increase in macrophage infiltration.
Conclusion: These findings highlight the critical roles of CXCL1 and CXCL2 in mounting an effective immune response against dematiaceous fungi and suggest their potential as therapeutic targets.
Keywords: CXCL1; CXCL2; Phialophora verrucosa; immune response.
© 2025 Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impairment of Immune Response against Dematiaceous Fungi in Card9 Knockout Mice.Mycopathologia. 2016 Oct;181(9-10):631-42. doi: 10.1007/s11046-016-0029-0. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Mycopathologia. 2016. PMID: 27421992
-
Langhans giant cells regulate cutaneous immune responses during mycobacterial infection through CXCL1/CXCL2 secretion.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;152:114447. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114447. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40088869
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Serve as Key Effector Molecules in the Protection Against Phialophora verrucosa.Mycopathologia. 2021 Jun;186(3):367-375. doi: 10.1007/s11046-021-00554-0. Epub 2021 May 19. Mycopathologia. 2021. PMID: 34013384 Free PMC article.
-
Phialophora verrucosa as a cause of deep infection following total knee arthroplasty.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2013 Nov;42(11):515-8. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2013. PMID: 24340322 Review.
-
Case report. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Phialophora verrucosa developed in a patient with non-HIV acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.Mycoses. 2002 Feb;45(1-2):50-4. Mycoses. 2002. PMID: 11856438 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

