CardioAI: A Multimodal AI-based System to Support Symptom Monitoring and Risk Prediction of Cancer Treatment-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 40391282
- PMCID: PMC12087674
- DOI: 10.1145/3706598.3714272
CardioAI: A Multimodal AI-based System to Support Symptom Monitoring and Risk Prediction of Cancer Treatment-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Abstract
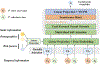
Despite recent advances in cancer treatments that prolong patients' lives, treatment-induced cardiotoxicity (i.e., the various heart damages caused by cancer treatments) emerges as one major side effect. The clinical decision-making process of cardiotoxicity is challenging, as early symptoms may happen in non-clinical settings and are too subtle to be noticed until life-threatening events occur at a later stage; clinicians already have a high workload focusing on the cancer treatment, no additional effort to spare on the cardiotoxicity side effect. Our project starts with a participatory design study with 11 clinicians to understand their decision-making practices and their feedback on an initial design of an AI-based decision-support system. Based on their feedback, we then propose a multimodal AI system, CardioAI, that can integrate wearables data and voice assistant data to model a patient's cardiotoxicity risk to support clinicians' decision-making. We conclude our paper with a small-scale heuristic evaluation with four experts and the discussion of future design considerations.
Keywords: Cancer treatment-induced cardiotoxicity; Human-AI collaboration; Large Language Models; Multimodal AI system.
Figures


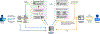
Similar articles
-
Rethinking Human-AI Collaboration in Complex Medical Decision Making: A Case Study in Sepsis Diagnosis.Proc SIGCHI Conf Hum Factor Comput Syst. 2024 May;2024:445. doi: 10.1145/3613904.3642343. Epub 2024 May 11. Proc SIGCHI Conf Hum Factor Comput Syst. 2024. PMID: 38835626 Free PMC article.
-
Adapting Artificial Intelligence Concepts to Enhance Clinical Decision-Making: A Hybrid Intelligence Framework.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Nov 19;17:5417-5422. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S497753. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39582919 Free PMC article.
-
Intricacies of Human-AI Interaction in Dynamic Decision-Making for Precision Oncology: A Case Study in Response-Adaptive Radiotherapy.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 30:2024.04.27.24306434. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.27.24306434. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 29;16(1):1138. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55259-x. PMID: 38746238 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Utilizing large language models for gastroenterology research: a conceptual framework.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 1;18:17562848251328577. doi: 10.1177/17562848251328577. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40171241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications, challenges and future directions of artificial intelligence in cardio-oncology.Eur J Clin Invest. 2025 Apr;55 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):e14370. doi: 10.1111/eci.14370. Eur J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 40191923 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Mutation to Prognosis: AI-HOPE-PI3K Enables Artificial Intelligence Agent-Driven Integration of PI3K Pathway Data in Colorectal Cancer Precision Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 5;26(13):6487. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136487. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed Bouatmane, Abdelaziz Daaif, and Abdelmajid Bousselham. 2024. Advancements in Cardiotoxicity Detection and Assessment through Artificial Intelligence: A Comprehensive Review. In 2024 4th International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology (IRASET). IEEE, 1–8.
-
- Albahri Ahmed Shihab, Duhaim Ali M, Fadhel Mohammed A, Alnoor Alhamzah, Baqer Noor S, Alzubaidi Laith, Albahri Osamah Shihab, Alamoodi Abdullah Hussein, Bai Jinshuai, Salhi Asma, et al. 2023. A systematic review of trustworthy and explainable artificial intelligence in healthcare: Assessment of quality, bias risk, and data fusion. Information Fusion 96 (2023), 156–191.
-
- Alvi Raza M, Frigault Matthew J, Fradley Michael G, Jain Michael D, Mahmood Syed S, Awadalla Magid, Lee Dae Hyun, Zlotoff Daniel A, Zhang Lili, Drobni Zsofia D, et al. 2019. Cardiovascular events among adults treated with chimeric antigen receptor T-cells (CAR-T). Journal of the American College of Cardiology 74, 25 (2019), 3099–3108. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amershi Saleema, Weld Dan, Vorvoreanu Mihaela, Fourney Adam, Nushi Besmira, Collisson Penny, Suh Jina, Iqbal Shamsi, Bennett Paul N, Inkpen Kori, et al. 2019. Guidelines for human-AI interaction. In Proceedings of the 2019 chi conference on human factors in computing systems. 1–13.
-
- Baig Mirza Mansoor, GholamHosseini Hamid, Moqeem Aasia A, Mirza Farhaan, and Lindén Maria. 2017. A systematic review of wearable patient monitoring systems–current challenges and opportunities for clinical adoption. Journal of medical systems 41 (2017), 1–9. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
