Psychosocial profiles and motivations for adolescent engagement in hazardous games: the role of boredom, peer influence, and self-harm tendencies
- PMID: 40391293
- PMCID: PMC12086149
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1527168
Psychosocial profiles and motivations for adolescent engagement in hazardous games: the role of boredom, peer influence, and self-harm tendencies
Abstract
Background: Adolescents' engagement in hazardous games has increased in recent years, presenting significant risks to physical and psychological well-being. These behaviors are often driven by complex psychosocial factors, including boredom, peer influence, and impulsivity. Understanding the specific motivations and profiles within this demographic is essential for developing effective interventions. Aims. This study aims to identify distinct adolescent profiles based on key psychosocial factors influencing engagement in hazardous games and to determine the primary predictors of risk-taking behavior. By exploring these profiles, we seek to inform targeted intervention strategies that address the unique needs of each group.
Methods: A sample of adolescents was assessed using standardized measures of boredom susceptibility, social influence, impulsivity, and self-harm tendencies. Cluster analysis was employed to categorize participants into distinct profiles, and regression analysis identified significant predictors of engagement in hazardous games. Descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze differences across profiles.
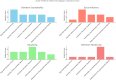
Results: Four primary profiles emerged: High-Risk Boredom-Prone, Socially Influenced Risk-Takers, Impulsive Sensation-Seekers, and Vulnerable and Self-Destructive. Boredom susceptibility and social influence were found to be the strongest predictors of hazardous game participation. High-Risk Boredom-Prone adolescents were driven by a need for stimulation, while Socially Influenced Risk-Takers prioritized peer approval. The Impulsive Sensation-Seekers cluster showed a strong tendency toward thrill-seeking, and the Vulnerable and Self-Destructive profile indicated a coping mechanism linked to emotional distress.
Conclusion: The findings highlight the importance of tailored interventions for adolescents, focusing on boredom management, peer resilience, and mental health support. Addressing these psychosocial drivers can help reduce the risks associated with hazardous games and support healthier developmental pathways. Future research should explore longitudinal data to track changes in adolescent risk behaviors over time and assess the impact of targeted interventions on each identified profile.
Keywords: adolescent risk behavior; boredom susceptibility; cluster analysis; hazardous games; impulsivity; peer influence; psychosocial factors; self-harm tendencies.
Copyright © 2025 Mancone, Celia, Zanon, Gentile and Diotaiuti.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Blakemore S-J. Avoiding social risk in adolescence. Curr Dir psychol Sci. (2018) 27:116–22. doi: 10.1177/0963721417738144 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources