Development, optimization and integrated characterization of rice-based yogurt alternatives enriched with roasted and non-roasted sprouted barley flour
- PMID: 40391379
- PMCID: PMC12088763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2025.101059
Development, optimization and integrated characterization of rice-based yogurt alternatives enriched with roasted and non-roasted sprouted barley flour
Abstract
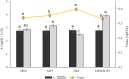
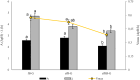
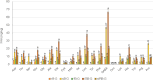
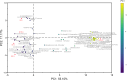
Plant-based yogurt substitutes ("gurts"), whose market growth is steadily increasing, have emerged as a promising option to promote more sustainable diets and food systems, especially when produced with locally sourced or low-input crops like barley. In this study, a novel gurt made with rice (10 %) and sprouted barley (5 %), was designed. Four lactic acid bacteria strains, Levilactobacillus brevis AM7, Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides DSM20193, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 18S9 and H64, were used as starters for making prototypes. Although with some differences in their acidification kinetics and proteolysis, all the strains adapted to the matrix. Then the formulation and production process were optimized. The use of sprouted barley, compared to raw flours, provided a content of amino acids 9-fold higher, further increased (up to 35 %) by the fermentation, and a more complex aroma profile characterized by the presence of furans and aldehydes. However, the high amylolytic activity in sprouted barley interfered with starch gelatinization decreasing the viscosity of the products from 3.3 to 0.08 Pa∗s. To overcome this challenge and obtain a creamy and spoonable product, sprouted barley flour was roasted, deactivating the enzymes and conferring a nutty and toasted flavor to the gurts due to the presence of pyrazines. The stability of the key biochemical and microbiological parameters during refrigerated storage was also assessed. Hence, plant-based gurts made with sprouted barley, emerge as a sustainable and health-promoting substitute to traditional dairy yogurts.
Keywords: Fermentation; GABA; Germination; Sprouted barley; Viscosity; Yogurt alternatives.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tailor-made fermentation of sprouted wheat and barley flours and their application in bread making: A comprehensive comparison with conventional approaches in the baking industry.Curr Res Food Sci. 2025 Apr 12;10:101053. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2025.101053. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40290370 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Selected Lactic Acid Bacteria and Carob Flour for the Production of a High-Fibre and "Clean Label" Plant-Based Yogurt-like Product.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 18;11(6):1607. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061607. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37375109 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a Plant-Based Yogurt-Like Product Fortified with Hemp Flour: Formulation and Characterization.Foods. 2023 Jan 20;12(3):485. doi: 10.3390/foods12030485. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36766014 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional properties and health aspects of pulses and their use in plant-based yogurt alternatives.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2021 Jul;20(4):3858-3880. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12778. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2021. PMID: 34125502 Review.
-
Invited review: Advances in yogurt development-Microbiological safety, quality, functionality, sensory evaluation, and consumer perceptions across different dairy and plant-based alternative sources.J Dairy Sci. 2025 Jan;108(1):33-58. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-25322. Epub 2024 Oct 5. J Dairy Sci. 2025. PMID: 39369892 Review.
References
-
- Cáceres P.J., Peñas E., Martínez-Villaluenga C., García-Mora P., Frías J. Development of a multifunctional yogurt-like product from germinated brown rice. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 2019;99:306–312. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.10.008. - DOI
-
- Carlsson Kanyama A., Hedin B., Katzeff C. Differences in environmental impact between plant-based alternatives to dairy and dairy products: a systematic literature review. Sustainability. 2021;13(22) doi: 10.3390/su132212599. - DOI
-
- Cheng W., Sun Y., Xia X., Yang L., Fan M., Li Y., Wang L., Qian H. Effects of β-amylase treatment conditions on the gelatinization and retrogradation characteristics of wheat starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2022;124 doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107286. - DOI
-
- Demarinis C., Montemurro M., Torreggiani A., Pontonio E., Verni M., Rizzello C.G. Use of selected lactic acid bacteria and carob flour for the production of a high-fibre and “clean label” plant-based yogurt-like product. Microorganisms. 2023;11(6):1607. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061607. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

