The SmWRKY32-SmbHLH65/SmbHLH85 regulatory module mediates tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- PMID: 40391389
- PMCID: PMC12087451
- DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhaf096
The SmWRKY32-SmbHLH65/SmbHLH85 regulatory module mediates tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza
Abstract
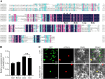
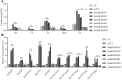
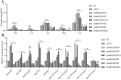
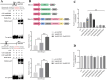
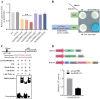
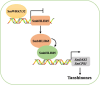
Tanshinones are valuable compounds found in Salvia miltiorrhiza, and gaining a deeper understanding of their transcriptional regulation mechanisms is a key strategy for increasing their content. Previous research revealed that SmWRKY32 acts as a repressor of tanshinone synthesis. This study identified the SmbHLH65 transcription factor, whose expression was significantly reduced in the SmWRKY32 overexpression transcriptome. Overexpression of SmbHLH65 stimulated tanshinone accumulation, while its silencing resulted in a decrease in tanshinone content. However, SmbHLH65 does not directly target the key enzyme genes involved in tanshinone synthesis. Subsequently, we discovered the SmbHLH65-interacting protein SmbHLH85. SmbHLH85 facilitates tanshinone biosynthesis by directly upregulating SmDXS2 and SmCPS1. Further investigation demonstrated that SmbHLH65 not only promotes the expression of SmbHLH85 but also enhances its binding to the promoters of SmDXS2 and SmCPS1, thereby amplifying the activation of these biosynthetic genes. Additionally, SmWRKY32 directly binds to the SmbHLH65 promoter to suppress its activity. In summary, these findings reveal that the regulatory module SmWRKY32-SmbHLH65/SmbHLH85 controls tanshinone synthesis in S. miltiorrhiza. This study uncovers a novel transcriptional regulatory mechanism, offering fresh insights into the complex network controlling tanshinone biosynthesis.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nanjing Agricultural University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The ethylene response factor SmERF6 co-regulates the transcription of SmCPS1 and SmKSL1 and is involved in tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots.Planta. 2018 Jul;248(1):243-255. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2884-z. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Planta. 2018. PMID: 29704055
-
The SmMYB36-SmERF6/SmERF115 module regulates the biosynthesis of tanshinones and phenolic acids in salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots.Hortic Res. 2022 Oct 26;10(1):uhac238. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac238. eCollection 2023. Hortic Res. 2022. PMID: 36643739 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of SmSCR1 Promotes Tanshinone Accumulation and Hairy Root Growth in Salvia miltiorrhiza.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 8;13:860033. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.860033. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35350294 Free PMC article.
-
New insights of advanced biotechnological engineering strategies for tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza.Plant Sci. 2025 Mar;352:112384. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2025.112384. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39756484 Review.
-
Transcription Factor: A Powerful Tool to Regulate Biosynthesis of Active Ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Feb 24;12:622011. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.622011. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33719294 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mei X, Cao Y, Che Y. et al. Danshen: a phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Chin J Nat Med. 2019;17:59–80 - PubMed
-
- Dai Z, Cui G, Zhou S. et al. Cloning and characterization of a novel 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase gene from Salvia miltiorrhiza involved in diterpenoid tanshinone accumulation. Plant Physiol. 2011;168:148–57 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

