RF shimming strategy for an open 60-channel RF transmit 7T MRI head coil for routine use on the single transmit mode
- PMID: 40391665
- PMCID: PMC12309876
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.30563
RF shimming strategy for an open 60-channel RF transmit 7T MRI head coil for routine use on the single transmit mode
Abstract
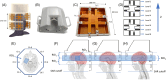
Purpose: To develop an radiofrequency (RF) shimming approach for operating the 2nd Generation Tic Tac Toe RF coil system (60 transmit channels integrated with 32-channel receive insert) for routine use in 7T neuro MRI on the single transmit mode.
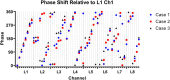
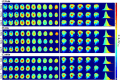
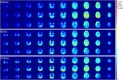
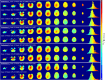
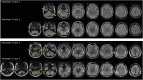
Methods: RF simulations were performed and used to develop non-subject-specific RF shim cases over three anatomically detailed head models: adult male, adult female, and child female. Multi-ROI shimming strategies were developed and implemented. maps and in vivo images were acquired on the single transmit mode of a 7T scanner using the RF shim cases derived from the computer simulations.
Results: The availability of 60 transmit channels enables more control over efficiency, specific absorption rate (SAR) efficiency, and homogeneity using RF shimming. On the single transmit mode, the 2nd generation Tic Tac Toe RF coil system consistently provides homogeneous field distribution with extended coverage into the temporal lobes, cerebellum, reaching all the way to C5-C6. Safe levels of SAR are also achieved.
Conclusion: By using a non-subject specific RF shimming approach derived from computer simulations, the 2nd generation Tic Tac Toe RF coil system allows for robust, routine neuroimaging (>1750 in vivo scanning sessions over the past 28 months) at 7T in single transmit mode.
Keywords: 7T RF coils; B1 field; RF shimming; SAR; Tic Tac Toe Design.
© 2025 The Author(s). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R56 AG074467/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH119168/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- OAC-2117681/National Science Foundation Office of Advanced Cyberinfrastructure
- T32MH119168/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH111265/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028483/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG063525/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH111265/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10OD028483/National Institutes of Health Office of Research Infrastructure Programs
- R01 AG063525/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1747452/National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program
- R56AG074467/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

