Changes in Generations of PAMAM Dendrimers and Compositions of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles Govern Delivery and Immune Recognition
- PMID: 40391736
- PMCID: PMC12152843
- DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5c00336
Changes in Generations of PAMAM Dendrimers and Compositions of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles Govern Delivery and Immune Recognition
Abstract
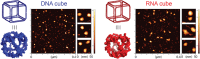
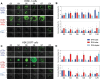
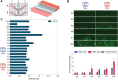
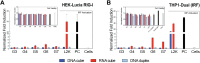
Nucleic acid nanoparticles (NANPs) are promising immune modulators due to their well-established structural properties and distinct structure-activity relationship with the immune system. We previously identified that NANPs' size, shape, composition, and type of delivery vehicle define their uptake by immune cells and subsequently induced cytokine profile. In this work, we examined the delivery efficiencies and immunological impacts of two representative NANPs─DNA cubes and RNA cubes─complexed with a benchmark delivery vehicle, Lipofectamine 2000 vs. different generations of amine-terminated poly(amidoamine) dendrimers. Using molecular dynamics simulations, we modeled dendrimer interactions with nucleic acid cargos. Next, we used traditional 2D and more recently established 3D cell cultures to assess dendrimers' influence on NANPs uptake. Immune activation was evaluated in several cell lines engineered with reporter genes driven by key immune signaling pathways. Specifically, HEK-lucia reporter cells were used to evaluate RIG-I activation, while THP1-Dual cells provided quantitative readouts for both IRF and NF-κB transcription factor activity. Our findings demonstrate that both dendrimer generation and NANP composition influence cellular uptake and immune responses. This study underscores the importance of formulation in shaping NANPs' biological properties and further advances the understanding of their immunological properties critical for the development of NANPs-based adjuvants.
Keywords: NANPs; PAMAM dendrimers; delivery; immune response; interferons; spheroids.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of PAMAM Dendrimers for the Delivery of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2709:253-259. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3417-2_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37572286 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Cytokines by Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles (NANPs) Depends on the Type of Delivery Carrier.Molecules. 2021 Jan 27;26(3):652. doi: 10.3390/molecules26030652. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33513786 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Recognition of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles (NANPs) in Human Primary Blood Cells.Molecules. 2019 Mar 20;24(6):1094. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061094. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30897721 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleic acid nanoparticles (NANPs) as molecular tools to direct desirable and avoid undesirable immunological effects.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Jun;173:427-438. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.04.011. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33857556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Recognition of and Reactions to Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles by Human Immune Cells.Molecules. 2021 Jul 12;26(14):4231. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144231. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299506 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
