Secreted phospholipase A2 regulates intercellular communications by coordinating extracellular phospholipid metabolism
- PMID: 40391916
- PMCID: PMC12421130
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxaf027
Secreted phospholipase A2 regulates intercellular communications by coordinating extracellular phospholipid metabolism
Abstract
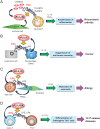
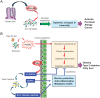
Lipids play fundamental roles in life. In essence, "phospholipase A2" (PLA2) indicates a group of enzymes that release fatty acids and lysophospholipids by hydrolyzing the sn-2 position of glycerophospholipids. To date, more than 50 enzymes that possess PLA2 or related lipid-metabolizing activities have been identified in mammals and are subdivided into several families in terms of their structures, catalytic mechanisms, tissue/cellular localizations, and evolutionary relationships. Among the PLA2 superfamily, the secreted PLA2 (sPLA2) family contains 11 isoforms in mammals, each of which has unique substrate specificity and tissue/cellular distributions. Recent studies using gene-manipulated (knockout and/or transgenic) mice for a full set of sPLA2s have revealed their diverse roles in immunity, metabolism, and other biological events. Application of mass spectrometric lipidomics to these mice has allowed the identification of target substrates and products of individual sPLA2s in tissue microenvironments. In principle, sPLA2s hydrolyze extracellular phospholipids such as those in extracellular vesicles, microbes, lipoproteins, surfactants, and ingested foods, as well as phospholipids in the plasma membrane of activated or damaged cells, thereby exacerbating or ameliorating various diseases. The actions of sPLA2s are dependent on, or independent of, the generation of free fatty acids, lysophospholipids, or their metabolites (lipid mediators) according to pathophysiological contexts. In this review, I will make an overview of recent understanding of the unexplored immunoregulatory roles of sPLA2s and their underlying lipid pathways, especially focusing on their unique actions on extracellular vesicles, activated/damaged cells, and gut microbiota.
Keywords: extracellular vesicle; lipid mediator; lipidomics; metabolism; microbiome.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Society for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Murakami M. The phospholipase A2 superfamily as a central hub of bioactive lipids and beyond. Pharmacol Ther 2023;244:108382. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108382 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murakami M, Sato H, Taketomi Y.. Updating phospholipase A2 biology. Biomolecules 2020;10:1457. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/biom10101457 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murakami M, Taketomi Y, Miki Y, et al. Recent progress in phospholipase A2 research: from cells to animals to humans. Prog Lipid Res 2011;50:152–92. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.plipres.2010.12.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dennis EA, Cao J, Hsu YH, et al. Phospholipase A2 enzymes: physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention. Chem Rev 2011;111:6130–85. https://doi.org/ 10.1021/cr200085w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shimizu T. Lipid mediators in health and disease: enzymes and receptors as therapeutic targets for the regulation of immunity and inflammation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2009;49:123–50. https://doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.011008.145616 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

