Impact of fixed appliance treatment on root resorption in root canal-treated teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40392039
- PMCID: PMC12138387
- DOI: 10.2340/aos.v84.43642
Impact of fixed appliance treatment on root resorption in root canal-treated teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: The relationship between orthodontic treatment and root resorption in endodontically treated teeth remains controversial. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effects of fixed appliance treatment on root resorption in root canal-treated teeth compared to vital teeth.
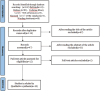
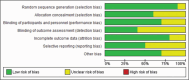
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted across multiple databases including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Sinomed, CNKI, and Wanfang. Studies comparing root resorption between root canal-treated teeth and vital teeth during orthodontic treatment were included. The methodological quality was assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using random-effects models.
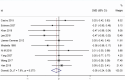
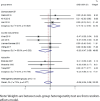
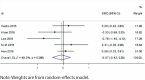
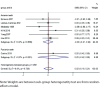
Results: Ten studies involving 266 patients met the inclusion criteria. The overall effect showed no significant difference in root resorption between root canal-treated teeth and vital teeth (SMD = -0.08, 95% CI: -0.24 to 0.08, I² = 7.0%). Subgroup analyses revealed no significant differences based on measurement methods, extraction versus non-extraction treatment, or tooth position. However, extraction cases demonstrated a numerical trend toward greater root resorption in root canal-treated teeth (SMD = -0.70, 95% CI: -1.50 to 0.11, I² = 67.1%, p = 0.048), while the non-extraction group showed no meaningful differences (SMD = -0.07, 95% CI: -0.42 to 0.28, I² = 49.2%, p = 0.096).
Conclusions: This meta-analysis suggests that root canal-treated teeth do not show significantly different root resorption patterns compared to vital teeth during orthodontic treatment. However, extraction cases may require careful monitoring due to a tendency toward increased root resorption.
Conflict of interest statement
All of the authors had no personal, financial, commercial, or academic conflicts of interest separately.
Figures


References
-
- Attavar S. An overview of the antimicrobial effect of natural irrigants in disinfection of root canal system. Pharmacophore. 2022;13(1):79–82. 10.51847/PpJg04CzT9 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

