Glycopolymer-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for the Detection of Western Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) Venom
- PMID: 40392118
- PMCID: PMC12152936
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5c00125
Glycopolymer-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for the Detection of Western Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) Venom
Abstract
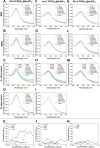
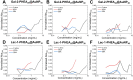
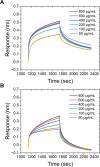
Every 5 minutes, 50 people are bitten by a snake worldwide; four will be permanently disabled and one will die. Most approaches to treating and diagnosing snake envenomation, a World Health Organization (WHO)-neglected tropical disease, rely on antibody-based solutions derived from animals or cell culture. Here, we present the first proof of concept for a glycopolymer-based ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) assay to detect snake venom, specifically Western Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) venom. This was achieved by synthesizing a library of glycan-terminated poly(hydroxyethyl acrylamide) functionalized gold nanoparticles. The library was analyzed using UV-vis spectroscopy and biolayer interferometry, with galactose-terminating systems found to demonstrate specificity for C. atrox venom, versus model lectins and Naja naja venom in UV-vis assays. This corroborates glycan array data in the literature and highlights our glycopolymer systems' potential as a diagnostic tool for snakebite, with the best particle system displaying a limit of detection of ∼20 μg·mL-1.
Figures


References
-
- Roberts N. L. S., Johnson E. K., Zeng S. M., Hamilton E. B., Abdoli A., Alahdab F., Alipour V., Ancuceanu R., Andrei C. L., Anvari D., Arabloo J., Ausloos M., Awedew A. F., Badiye A. D., Bakkannavar S. M., Bhalla A., Bhardwaj N., Bhardwaj P., Bhaumik S., Bijani A., Boloor A., Cai T., Carvalho F., Chu D. T., Couto R. A. S., Dai X., Desta A. A., Do H. T., Earl L., Eftekhari A., Esmaeilzadeh F., Farzadfar F., Fernandes E., Filip I., Foroutan M., Franklin R. C., Gaidhane A. M., Gebregiorgis B. G., Gebremichael B., Ghashghaee A., Golechha M., Hamidi S., Haque S. E., Hayat K., Herteliu C., Ilesanmi O. S., Islam M. M., Jagnoor J., Kanchan T., Kapoor N., Khan E. A., Khatib M. N., Khundkar R., Krishan K., Kumar G. A., Kumar N., Landires I., Lim S. S., Madadin M., Maled V., Manafi N., Marczak L. B., Menezes R. G., Meretoja T. J., Miller T. R., Mohammadian-Hafshejani A., Mokdad A. H., Monteiro F. N. P., Moradi M., Nayak V. C., Nguyen C. T., Nguyen H. L. T., Nuñez-Samudio V., Ostroff S. M., Padubidri J. R., Pham H. Q., Pinheiro M., Pirestani M., Quazi Syed Z., Rabiee N., Radfar A., Rahimi-Movaghar V., Rao S. J., Rastogi P., Rawaf D. L., Rawaf S., Reiner R. C., Sahebkar A., Samy A. M., Sawhney M., Schwebel D. C., Senthilkumaran S., Shaikh M. A., Skryabin V. Y., Skryabina A. A., Soheili A., Stokes M. A., Thapar R., Tovani-Palone M. R., Tran B. X., Travillian R. S., Velazquez D. Z., Zhang Z. J., Naghavi M., Dandona R., Dandona L., James S. L., Pigott D. M., Murray C. J. L., Hay S. I., Vos T., Ong K. L.. Global Mortality of Snakebite Envenoming between 1990 and 2019. Nat. Commun. 2022;13(1):6160. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33627-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pintor A. F. V., Ray N., Longbottom J., Bravo-Vega C. A., Yousefi M., Murray K. A., Ediriweera D. S., Diggle P. J.. Addressing the Global Snakebite Crisis with Geo-Spatial Analyses – Recent Advances and Future Direction. Toxicon X. 2021;11:100076. doi: 10.1016/j.toxcx.2021.100076. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ratanabanangkoon K.. Merit and Demerit of Polyvalent Snake Antivenoms. J. Toxicol., Toxin Rev. 2003;22(1):77–89. doi: 10.1081/TXR-120019563. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

