Visfatin promotes multiple myeloma cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by inducing IL-6 production via NF-κB pathways
- PMID: 40392374
- PMCID: PMC12092901
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02682-1
Visfatin promotes multiple myeloma cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by inducing IL-6 production via NF-κB pathways
Abstract
Background: Multiple myeloma (MM) is the second most prevalent hematological malignancy that results in the proliferation of malignant plasma cells and the overproduction of monoclonal immunoglobulin. Visfatin plays an important role in the regulation of apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation; however, to this date, the role of visfatin in multiple myeloma is unclear.
Objective: To explore the role of visfatin in multiple myeloma and find new targets for MM treatment.
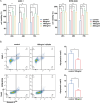
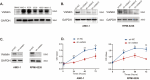
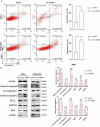
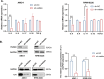
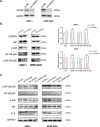
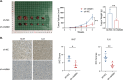
Methods: In this study, expression of visfatin in bone marrow was detected by ELISA. The diagnostic value of visfatin was determined by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. After the quality control by performing western blot to confirm the knockdown of visfatin in two MM cell lines, the phenotype (proliferation and apoptosis) of visfatin in MM was determined by carrying out in vitro experiments, including CCK8, flow cytometry, and western blot. Several cytokines were determined by real-time PCR, followed by in vivo experiments and immunohistochemical assays. IκB, NF-κbp65, and phosphorylation were determined by western blot.
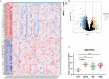
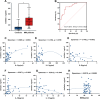
Results: We found that visfatin level increased in the bone marrow of MM patients compared to controls. ROC curve analysis result showed that bone marrow visfatin was able to distinguish MM patients from controls. In vitro and in vivo, visfatin promotes MM cell proliferation. The production of IL-6 was attenuated by visfatin knockdown. Furthermore, we showed that visfatin could activate IL-6 production via the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Conclusions: In MM, visfatin promotes tumor progression by upregulating IL-6 production, which may be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of MM patients.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Interleukin-6; Multiple myeloma; Nuclear factor kappa-B; Visfatin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by Ethical Committee of Lanzhou University Second Hospital according to the Declaration of Helsinki. All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the Guidelines for endpoints in animal study proposals. All the procedures used in these experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of Lanzhou University Second Hospital. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CCN1 Promotes Inflammation by Inducing IL-6 Production via α6β1/PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Pathway in Autoimmune Hepatitis.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 25;13:810671. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.810671. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35547732 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-34a and MicroRNA-181a Mediate Visfatin-Induced Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via NF-κB Pathway in Human Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes.Cells. 2019 Aug 11;8(8):874. doi: 10.3390/cells8080874. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31405216 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Mediate Visfatin and Resistin Induction of Oxidative Stress in Human Osteoarthritic Synovial Fibroblasts Via NF-κB Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 20;20(20):5200. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205200. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31635187 Free PMC article.
-
Increased visfatin expression is associated with nuclear factor-kappa B and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in periodontal inflammation.Clin Oral Investig. 2017 May;21(4):1113-1121. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1871-7. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Clin Oral Investig. 2017. PMID: 27283324
-
The NF-κB Activating Pathways in Multiple Myeloma.Biomedicines. 2018 May 16;6(2):59. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6020059. Biomedicines. 2018. PMID: 29772694 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
