Enhanced prognosis and regional cooperative rescue systems for acute myocardial infarction: insights from chest pain centers in Ningxia, China
- PMID: 40392480
- PMCID: PMC12331797
- DOI: 10.1007/s11739-025-03962-y
Enhanced prognosis and regional cooperative rescue systems for acute myocardial infarction: insights from chest pain centers in Ningxia, China
Abstract
Chest Pain Centers (CPC) demonstrated improved outcomes for patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) globally. However, the long-term impact of CPC establishment in economically developing areas, such as Ningxia, China, remains unclear. This study aimed to assess the long-term prognosis and efficacy of collaborative regional rescue systems centered on CPC for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients in Ningxia. This retrospective cohort study analyzed 5344 STEMI patients from the Ningxia Myocardial Infarction Registry (2014-2019). Based on CPC establishment, patients were segregated into two groups: pre-CPC (n = 2141) and post-CPC (n = 3203). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazards models were employed to compare the groups and evaluate long-term outcomes, including mortality and major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (MACCEs). A total of 5344 acute STEMI patients were included, with 2141 (40.06%) in the pre-CPC group and 3203 (59.94%) in the post-CPC group. In comparison to the pre-CPC group, the post-CPC group exhibited lower all-cause mortality rates at 30 days (4.53% vs. 6.68%, p = 0.001), 1 year (6.24% vs. 9.11%, p = 0.001), and 3 years (8.55% vs. 11.86%, p < 0.001). Additionally, the post-CPC group showed decreased rates of MACCEs at 30 days (7.90% vs. 10.00%, p = 0.008) and 3 years (18.86% vs. 23.12%, p < 0.001). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis yielded similar results. After adjusting for confounding factors using COX multivariable regression, the CPC establishment was found to be a protective factor for all-cause mortality and MACCEs within 30 days (MACCEs: HR = 0.72, 95%CI 0.59-0.88, p = 0.005; all-cause mortality: HR = 0.59, 95%CI 0.46-0.77, p < 0.001), 1 year (MACCEs events: HR = 0.80, 95%CI 0.68-0.94, p = 0.006; all-cause mortality: HR = 0.59, 95%CI 0.44-0.69, p < 0.001), and 3 years (MACCEs: HR = 0.71, 95%CI 0.62-0.81, p < 0.001; all-cause mortality: HR = 0.55, 95%CI 0.46-0.67, p < 0.001). The establishment of Chest Pain Centers and implementation of regional cooperative rescue systems significantly improved the long-term prognosis of STEMI patients in Ningxia. These findings underscore the importance of developing CPC in underdeveloped regions to enhance cardiovascular emergency care and reduce mortality and morbidity associated with acute myocardial infarction.
Keywords: Acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; Chest pain center; Prognosis; Reperfusion therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of the General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University (approval number 2020–774). As this was a retrospective study, and the requirement for informed consent was therefore waived. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Human and animal rights statement and informed consent: The study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of the General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University (approval number 2020–774). As this was a retrospective study, and the requirement for informed consent was therefore waived.
Figures
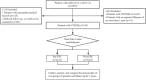
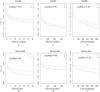

Similar articles
-
Beta-blockers in patients without heart failure after myocardial infarction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 5;11(11):CD012565. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012565.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34739733 Free PMC article.
-
The ratio of serum glucose to potassium is associated with poor prognosis in patients with severe acute myocardial infarction.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 7;15(1):28846. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14002-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40770037 Free PMC article.
-
Association of triglyceride-glucose index and estimated glucose disposal rate with outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction: Cumulative effect and mediation analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 23;20(7):e0328150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328150. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40700433 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of clinical features and outcomes of Chinese patients with Takotsubo syndrome and acute myocardial infarction-results from the first Chinese Takotsubo syndrome registry.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2025 Jun 30;15(3):563-573. doi: 10.21037/cdt-2025-8. Epub 2025 Jun 25. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2025. PMID: 40656782 Free PMC article.
-
Complete versus culprit-only revascularisation in ST elevation myocardial infarction with multi-vessel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 3;5(5):CD011986. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011986.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28470696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dong Z, Jing L, Miao W et al (2018) Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in China: current features and implications. Nat Rev Cardiol. 10.1038/s41569-018-0119-4 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

