Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-Alpha: a key regulator in liver carcinogenesis
- PMID: 40392499
- PMCID: PMC12238214
- DOI: 10.1007/s13402-025-01064-7
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-Alpha: a key regulator in liver carcinogenesis
Abstract
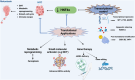
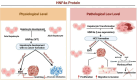
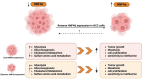
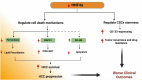
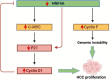
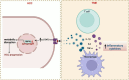
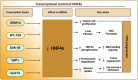
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality, associated with viral hepatitis, alcohol consumption, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4α), a crucial transcription factor for liver function (glucose and lipid metabolism, bile acid homeostasis, and cellular differentiation), is often dysregulated in HCC progression. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the role of HNF4α in hepatic oncogenesis, providing novel inshight into its regulatory effects on epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), metabolic alterations (including the Warburg effect), cell cycle control, and tumor microenvironment. We also discuss therapeutic strategies targeting HNF4α focusing on restoring metabolic balance and inducing apoptosis. This integrated analysis advances our understanding of HNF4α's contribution to HCC and may pave the way for the development of targeted therapies (Fig. 1).
Keywords: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; HNF4α; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Progression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated functional genomics-identified DEAF1 in oxidative stress and hepatocellular carcinoma development.Carcinogenesis. 2025 Apr 3;46(2):bgaf032. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgaf032. Carcinogenesis. 2025. PMID: 40554679
-
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma.Metabolism. 2016 Aug;65(8):1151-60. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.01.010. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Metabolism. 2016. PMID: 26907206
-
CYP4F11, an NRF2 Target Gene, Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Growth.Mol Carcinog. 2025 Jul;64(7):1264-1274. doi: 10.1002/mc.23925. Epub 2025 May 6. Mol Carcinog. 2025. PMID: 40329467
-
Spliced exon9 ADRM1 promotes liver oncogenicity via selective degradation of tumor suppressor FBXW7.J Hepatol. 2025 Jul;83(1):92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.12.037. Epub 2025 Jan 7. J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39788431
-
Role of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 Alpha in Liver Cancer.Semin Liver Dis. 2024 Aug;44(3):383-393. doi: 10.1055/a-2349-7236. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Semin Liver Dis. 2024. PMID: 38901435 Review.
References
-
- P. Konyn, A. Ahmed, D. Kim, Current epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15, 1295–1307 (2021). 10.1080/17474124.2021.1991792 - PubMed
-
- Z. Li, N. Zhang, Z. Dong, X. Wang, J. Zhou, J. Gao, Y. Yang, J. Li, F. Guan, Y. Zhou, Z. Tan, Integrating transcriptomics, glycomics and glycoproteomics to characterize hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Commun. Signal. 22, 200–215 (2024). 10.1186/s12964-024-01569-y - PMC - PubMed
-
- E. Haque, A.S. Teeli, D. Winiarczyk, M. Taguchi, S. Sakuraba, H. Kono, P. Leszczyński, M. Pierzchała, H. Taniguchi, HNF1A POU domain mutations found in Japanese liver Cancer patients cause downregulation of HNF4A promoter activity with possible disruption in transcription networks. Genes 13, 413–434 (2022). 10.3390/genes13030413 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- KC-23236563/Yunnan University
- 82273460, 82273089 and 32260167/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202401AS070133 and 202401AS070634/the Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects
- KLTIPT-2023-02 and KLTIPT-2023-03/Key Laboratory of Tumor Immunological Prevention and Treatment in Yunnan Province, Yan'an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

