Substance Use Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment Among Youth-Serving Clinicians
- PMID: 40392550
- PMCID: PMC12093189
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.11579
Substance Use Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment Among Youth-Serving Clinicians
Abstract
Importance: Despite decreasing substance use by adolescents in recent years, overdose rates continue to rise. Morbidity and mortality from substance use is preventable if detected; however, screening practices among youth-serving clinicians are unknown.
Objective: To describe youth-serving clinicians' screening, brief intervention, and referral to treatment practices for substance use disorders (SUDs) among adolescents.
Design, setting, and participants: This cross-sectional study used DocStyles data from September 5 to October 12, 2023, on clinical practice settings in the US. Responding clinicians included family physicians, internal medicine physicians, pediatricians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants.
Exposure: Delivery of services to youths aged 17 years or younger.
Main outcomes and measures: Screening, brief intervention, and referral to treatment practices, including screening frequency and type of screening tool used, and screening at every well visit using a screening tool were assessed using descriptive statistics and multivariable logistic regression.
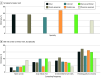
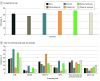
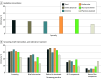
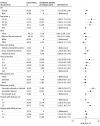
Results: Of 1047 youth-serving clinicians (mean [SD] age, 45.3 [11.4] years; 555 male [53.0%]), 467 (44.6%) were family physicians, 250 (23.9%) were pediatricians, 132 (12.6%) were internal medicine physicians, 107 (10.2%) were nurse practitioners, and 91 (8.7%) were physician assistants (survey response rate, 57%). Median years in practice was 13 (IQR, 7-23 years). Most clinicians (634 [60.6%]) reported that skills in SUD diagnosis were relevant to their practice, and 800 (76.4%) reported seeing at least 1 adolescent with an SUD monthly. A majority of clinicians (596 [56.9%]) reported screening for SUDs at every well visit, with a high proportion of pediatricians reporting screening at every well visit (173 of 250 [69.2%]). Clinicians who screened at every well visit were more likely to use a screening tool (odds ratio, 1.87 [95% CI, 1.44-2.44]). Only 411 clinicians (39.3%) reported screening at every well visit using a screening tool; 321 clinicians (30.7%) offered all components of screening, brief intervention, and referral to treatment practice. Clinicians who reported seeing 5 or more adolescents with an SUD per month had a higher odds of screening with a standardized tool at every annual well visit (adjusted odds ratio, 2.19 [95% CI, 1.30-3.71]).
Conclusions and relevance: These findings suggest that while most clinicians report screening youths for SUDs at least sometimes, a substantial proportion screened only intermittently. Efforts to improve screening rates through education and systems-based practice changes may facilitate offering anticipatory guidance and SUD treatment in all youth-serving clinical settings.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Psychological therapies for post-traumatic stress disorder and comorbid substance use disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 4;4(4):CD010204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27040448 Free PMC article.
-
Surveillance for Violent Deaths - National Violent Death Reporting System, 50 States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico, 2022.MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025 Jun 12;74(5):1-42. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7405a1. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025. PMID: 40493548 Free PMC article.
-
Incentives for preventing smoking in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 6;6(6):CD008645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008645.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28585288 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevention and Management of Opioid use Disorder and Overdose in Adolescents and Young Adults.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2025 Sep 12. doi: 10.1007/s11920-025-01638-0. Online ahead of print. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2025. PMID: 40938541 Review.
References
-
- 2023 NSDUH-illicit drug use. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Accessed July 30, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt47100/NSDUHDe...

