A Robust Cross-Platform Solution With the Sense2Quit System to Enhance Smoking Gesture Recognition: Model Development and Validation Study
- PMID: 40392581
- PMCID: PMC12134699
- DOI: 10.2196/67186
A Robust Cross-Platform Solution With the Sense2Quit System to Enhance Smoking Gesture Recognition: Model Development and Validation Study
Abstract
Background: Smoking is a leading cause of preventable death, and people with HIV have higher smoking rates and are more likely to experience smoking-related health issues. The Sense2Quit study introduces innovative advancements in smoking cessation technology by developing a comprehensive mobile app that integrates with smartwatches to provide real-time interventions for people with HIV attempting to quit smoking.
Objective: We aim to develop an accurate smoking cessation app that uses everyday smartwatches and an artificial intelligence model to enhance the recognition of smoking gestures by effectively addressing confounding hand gestures that mimic smoking, thereby reducing false positives. The app ensures seamless usability across Android (Open Handset Alliance [led by Google]) and iOS platforms, with optimized communication and synchronization between devices for real-time monitoring.
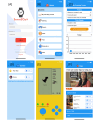
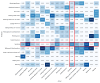
Methods: This study introduces the confounding resilient smoking model, specifically trained to distinguish smoking gestures from similar hand-to-mouth activities used by the Sense2Quit system. By incorporating confounding gestures into the model's training process, the system achieves high accuracy while maintaining efficiency on mobile devices. To validate the model, 30 participants, all people with HIV who smoked cigarettes, were recruited. Participants wore smartwatches on their wrists and performed various hand-to-mouth activities, including smoking and other gestures such as eating and drinking. Each participant spent 15 to 30 minutes completing the tasks, with each gesture lasting 5 seconds. The app was developed using the Flutter framework to ensure seamless functionality across Android and iOS platforms, with robust synchronization between the smartwatch and smartphone for real-time monitoring.
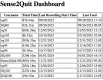
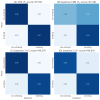
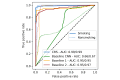
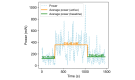
Results: The confounding resilient smoking model achieved an impressive F1-score of 97.52% in detecting smoking gestures, outperforming state-of-the-art models by distinguishing smoking from 15 other daily hand-to-mouth activities, including eating, drinking, and yawning. Its robustness and adaptability were further confirmed through leave-one-subject-out evaluation, demonstrating consistent reliability and generalizability across diverse individuals. The cross-platform app, developed using Flutter (Google), demonstrated consistent performance across Android and iOS devices, with only a 0.02-point difference in user experience ratings between the platforms (iOS 4.52 and Android 4.5). The app's continuous synchronization ensures accurate, real-time tracking of smoking behaviors, enhancing the system's overall utility for smoking cessation.
Conclusions: Sense2Quit represents a significant advancement in smoking cessation technology. It delivers timely, just-in-time interventions through innovations in cross-platform communication optimization and the effective recognition of confounding hand gestures. These improvements enhance the accuracy and accessibility of real-time smoking detection, making Sense2Quit a valuable tool for supporting long-term cessation efforts among people with HIV trying to quit smoking.
International registered report identifier (irrid): RR2-10.2196/49558.
Keywords: confounding gestures; convolutional neural networks; e-cigarette; mobile application; mobile health; mobile phone; people living with HIV; real-time monitoring; smartwatch; smoking cessation; smoking gestures; vaping; wearable technology.
©Anarghya Das, Juntao Feng, Maeve Brin, Patricia Cioe, Rebecca Schnall, Ming-Chun Huang, Wenyao Xu. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 20.05.2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pilot Testing of an mHealth App for Tobacco Cessation in People Living With HIV: Protocol for a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2023 Oct 19;12:e49558. doi: 10.2196/49558. JMIR Res Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37856173 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility and Acceptability of the Sense2Quit App for Improving Smoking Cessation in PWH.AIDS Behav. 2025 Jun;29(6):1920-1929. doi: 10.1007/s10461-025-04659-1. Epub 2025 Feb 25. AIDS Behav. 2025. PMID: 40000581 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Development and evaluation of visualizations of smoking data for integration into the Sense2Quit app for tobacco cessation.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2024 Jan 18;31(2):354-362. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocad162. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2024. PMID: 37632226 Free PMC article.
-
Smartphone Apps for Smoking Cessation: Systematic Framework for App Review and Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Jul 13;25:e45183. doi: 10.2196/45183. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37440305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smartphone Apps for Pulmonary Hypertension: Systematic Search and Content Evaluation.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2024 Oct 30;12:e57289. doi: 10.2196/57289. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2024. PMID: 39476376 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Validating the information technology (IT) implementation framework to Implement mHealth technology for consumers: A case study of the Sense2Quit app for smoking cessation.Int J Med Inform. 2025 Oct;202:105977. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2025.105977. Epub 2025 May 20. Int J Med Inform. 2025. PMID: 40413979
References
-
- Perez-Warnisher M, Carballosa de Miguel MDP, Seijo L. Tobacco use worldwide: legislative efforts to curb consumptiona. Ann Glob Health. 2019;85(1):9. doi: 10.5334/aogh.2417. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/30741510 9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- West R. Tobacco smoking: health impact, prevalence, correlates and interventions. Psychol Health. 2017;32(8):1018–1036. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2017.1325890. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/08870446.2017.1325890?url_ve... - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schnall R, Trujillo P, Alvarez G, Michaels CL, Brin M, Huang M, Chen H, Xu W, Cioe PA. Theoretically guided iterative design of the Sense2Quit app for tobacco cessation in persons living with HIV. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(5):4219. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20054219. https://www.mdpi.com/resolver?pii=ijerph20054219 ijerph20054219 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chu K, Matheny SJ, Escobar-Viera CG, Wessel C, Notier AE, Davis EM. Smartphone health apps for tobacco cessation: a systematic review. Addict Behav. 2021;112:106616. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106616. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32932102 S0306-4603(20)30746-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ghorai K, Akter S, Khatun F, Ray P. mHealth for smoking cessation programs: a systematic review. J Pers Med. 2014;4(3):412–423. doi: 10.3390/jpm4030412. https://www.mdpi.com/resolver?pii=jpm4030412 jpm4030412 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

