QSPR modeling of some COVID-19 drugs using neighborhood eccentricity-based topological indices: A comparative analysis
- PMID: 40392879
- PMCID: PMC12091765
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321359
QSPR modeling of some COVID-19 drugs using neighborhood eccentricity-based topological indices: A comparative analysis
Abstract
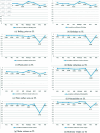
COVID-19, which emerged in 2019, is a disease caused by a new coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV-2), and has caused a worldwide epidemic. During and after this outbreak, it has been confirmed once again that finding a drug to prevent and end such diseases as soon as possible is an important issue. However, drug discovery and to determine a molecule's physical characteristics in a lab takes effort and time and is a costly process. Relevant information about molecules can be obtained by calculating topological indices, which are molecular descriptive numerical values corresponding to the physical properties of the chemical structure of a molecule. In this paper, we consider recently used drugs such as arbidol, chloroquine, hydroxy-chloroquine, lopinavir, remdesivir, ritonavir, thalidomide and theaflavin in treatment of COVID-19. This article examines neighborhood eccentricity-based topological descriptors that are used to analyze the structures of potential drugs against COVID-19. Eccentricity-based topological indices are advancing the field of chem-informatics and helping scientists better understand structure-activity correlations across a wide range of chemical compounds. The purpose is to identify structural components that have a significant impact on physico-chemical properties. In this context, the chemical structure and the corresponding molecular graph of the drugs under consideration are given in order to calculate the neighborhood eccentricity values. QSPR models are studied using linear and cubic regression analysis with topological indices for boiling point, enthalpy of vaporization, flash point, molar refraction, polar surface area, polarizability, molar volume and molecular weight properties of these drugs. Regression analysis is applied to find potential correlation between different drug characteristics such as bio-availability and efficacy. The results show that topological indices and applied regression models are useful in predicting significant characteristics of drugs used for the treatment of COVID-19. Additionally, a comparison of the known values and the calculated values from the regression models discussed is obtained.
Copyright: © 2025 Kara et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
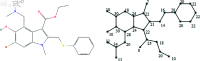
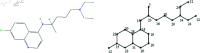
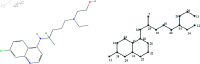

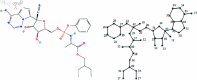
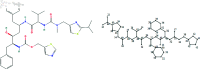
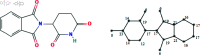

References
-
- World Health Organization. [cited 2024. May 28]. https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Chartrand G, Lesniak L. Graphs and digraphs. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRS Press; 2005.
-
- Gutman I. A property of the simple topological index. MATCH Commun Math Comput Chem. 1990;25:131–40.
-
- Devillers J, Balaban AT. Algorithms and software for the computation of topological indices and structure-property models. Topological indices and related descriptors in QSAR and QSPAR. 2000. p. 789–814.
-
- Omar R, Najar A, Bobtaina E, Elsheikh A. Pryazolylpyridine and triazolylpyridine derivative of hydroxychloroquine as potential therapeutic against COVID-19: theoretical evaluation. J Drug Deliv Therap. 2020;10(4):181–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

