An after-action review of COVID-19 cases and mitigation measures at US Mission India, March 2020-July 2021
- PMID: 40392896
- PMCID: PMC12091728
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0003982
An after-action review of COVID-19 cases and mitigation measures at US Mission India, March 2020-July 2021
Abstract
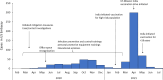
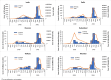
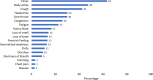
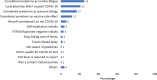
Between March 2020-June 2021, over 30 million COVID-19 cases were reported in India. We described the COVID-19 response across the US Mission India (US Embassy New Delhi, US Consulates - Mumbai, Hyderabad, Chennai, and Kolkata) to use the learnings for a possible future pandemic. We reviewed COVID-19 mitigation activities at five US Mission India posts from March 2020-July 2021. We also analyzed case investigation and contact tracing data from Health Units (outpatient clinics), including demographics, clinical findings, test results, contact positivity rate, and compared attack rates across the posts during the same period. The US Mission in India, comprising multiple US Government agencies, initiated COVID-19 mitigation in March 2020 with educational sessions, infection prevention training, health assessments, and standard operating procedures. The Health Unit and US CDC India office initiated COVID-19 case investigations and conducted contact tracing. During the study period, 636 COVID-19 cases (72% males), including 48 clusters (size range 2-10 cases), were reported. Overall case fatality rate was 1.5% (10). Of case patients, 82% (523) were Indians, and 18% (113) were Americans. On presentation, 22% (138/625) of cases were asymptomatic. The median time from symptom onset to notification to the Health Unit was three days (Interquartile range 1-5). The Health Unit identified 2,484 contacts with a 25% positivity rate. The attack rates ranged between 10-19%, with the highest at 19% in Delhi, which was lower compared to the estimated attack rate for respective cities but closely resembled the pattern of COVID-19 waves in India. Collaboration between medical providers and public health specialists during the COVID-19 response in US Mission India led to new organizational capabilities in contact tracing, community education, and workflows. These strategies helped reduce morbidity and mortality within the US Mission during the pandemic.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Johns Hopkins coronavirus resource center. COVID-19 map [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jul 31]. Available from https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
