Grocery shopping as an outcome measure: A scoping review
- PMID: 40392935
- PMCID: PMC12091886
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324711
Grocery shopping as an outcome measure: A scoping review
Abstract
Background: Grocery shopping is a complex Instrumental Activity of Daily Living (IADL) requiring cognitive and physical components that can be used to assess functional performance. Real-world physical and cognitive demands of grocery shopping occur simultaneously; however, many existing outcome measures only include a single domain or subtask. The objective of this review is to examine how grocery shopping as a whole, or multiple simultaneous subtasks of grocery shopping, has been used as a functional outcomes measure.
Methods: Peer-reviewed manuscripts in the English language were retrieved from PubMed, Medline, Scopus, and Cochrane published on or before December 20, 2024. Articles were included if an outcome measure included multiple subtasks of grocery shopping and excluded if an outcome was related to only a single subtask of grocery shopping. Extracted data included Author(s), Publication Title, Publication Year, Study Location, Study population, Grocery Setting (Virtual, Real-World, Simulated, or Patient Reported Answers), Grocery-specific measure, and Grocery-Specific outcome results.
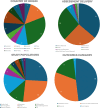
Results: Fifty-eight studies were included from 15 different countries. The most common populations studied were healthy adults (15) and psychiatric disorders (15). Common methods of assessment included patient-reported outcome measures (22), virtual reality (17), and physically simulated or real grocery shopping (20). Only three studies examined naturalistic, free-living grocery shopping. Outcomes were related to cognitive functioning (28), physical or motor impairments (23), or behavioral aspects of shopping (9).
Conclusions: This review provides critical insights into how grocery shopping has been adopted as a performance outcome measure across populations and testing environments. Despite the growing recognition of grocery shopping as a useful measure, gaps remain in the literature, especially related to a lack of studies that integrate cognitive and physical domains or explore its use in populations with combined cognitive and physical impairments.
Copyright: © 2025 Cole et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Occupational therapy for cognitive impairment in stroke patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 29;3(3):CD006430. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006430.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35349186 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- Occupational therapy practice framework: domain and process-fourth edition. Am J Occup Ther. 2020;74(Supplement_2):7412410010p1-p87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources