Microbial Dynamics on Different Microplastics in Coastal Urban Aquatic Ecosystems: The Critical Roles of Extracellular Polymeric Substances
- PMID: 40392941
- PMCID: PMC12139041
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.5c03796
Microbial Dynamics on Different Microplastics in Coastal Urban Aquatic Ecosystems: The Critical Roles of Extracellular Polymeric Substances
Abstract
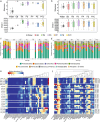
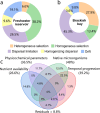
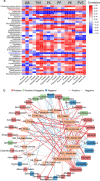
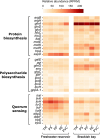
Microplastics (MPs) serve as carriers for microbial community colonization, forming unique ecosystems known as plastispheres in urban aquatic ecosystems. However, interactions among microbes, extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), and MPs remain poorly understood. This study investigates microbial consortia and their EPS secretion behaviors across various plastispheres at two representative coastal urban water sites. Permutational multivariate analysis of variance revealed that MP type significantly influenced microbial community structures in reservoir environments (R2 = 0.60, p < 0.001), highlighting the pronounced impact of MP types in high-quality urban waters. Specific microbial phyla and genera were identified as key contributors to EPS compositional variations across different plastispheres. Hierarchical partitioning results identified Acidobacteria, Nitrospirae, and Planctomycetes as influential phyla positively affecting EPS composition. Spearman correlation analysis pinpointed Robiginitialea (positive correlation) and Fimbriiglobus (negative correlation) as critical genera influencing EPS dynamics. Moreover, EPS-related gene abundance corresponded closely with observed EPS compositional differences. Dominant genes associated with protein biosynthesis included xapD in reservoirs and glnA in bays, while glmS and eno were predominant for polysaccharide biosynthesis in bays. This research advances our understanding of microbial-EPS-MP interactions in urban water systems, offering critical insights into ecological remediation and risk assessment of MP pollution.
Keywords: extracellular polymeric substances (EPS); metagenomic sequencing; microbial community; microplastics (MPs); temporal succession.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exposure of Goniopora columna to polyethylene microplastics (PE-MPs): Effects of PE-MP concentration on extracellular polymeric substances and microbial community.Chemosphere. 2022 Jun;297:134113. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134113. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35227744
-
Ecological responses of coral reef to polyethylene microplastics in community structure and extracellular polymeric substances.Environ Pollut. 2022 Aug 15;307:119522. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119522. Epub 2022 May 28. Environ Pollut. 2022. PMID: 35640726
-
Changes of the physicochemical properties of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from Microcystis aeruginosa in response to microplastics.Environ Pollut. 2022 Dec 15;315:120354. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120354. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Environ Pollut. 2022. PMID: 36215775
-
Impacts of extracellular polymeric substances on the behaviors of micro/nanoplastics in the water environment.Environ Pollut. 2023 Dec 1;338:122691. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.122691. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Environ Pollut. 2023. PMID: 37797922 Review.
-
Responses of natural plastisphere community and zooplankton to microplastic pollution: a review on novel remediation strategies.Arch Microbiol. 2025 May 7;207(6):136. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04334-y. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40332619 Review.
References
-
- Nava V., Chandra S., Aherne J., Alfonso M. B., Antao-Geraldes A. M., Attermeyer K., Bao R., Bartrons M., Berger S. A., Biernaczyk M., Bissen R., Brookes J. D., Brown D., Canedo-Argueelles M., Canle M., Capelli C., Carballeira R., Cereijo J. L., Chawchai S., Christensen S. T., Christoffersen K. S., de Eyto E., Delgado J., Dornan T. N., Doubek J. P., Dusaucy J., Erina O., Ersoy Z., Feuchtmayr H., Frezzotti M. L., Galafassi S., Gateuille D., Goncalves V., Grossart H.-P., Hamilton D. P., Harris T. D., Kangur K., Kankilic G. B., Kessler R., Kiel C., Krynak E. M., Leiva-Presa A., Lepori F., Matias M. G., Matsuzaki S.-I. S., McElarney Y., Messyasz B., Mitchell M., Mlambo M. C., Motitsoe S. N., Nandini S., Orlandi V., Owens C., Ozkundakci D., Pinnow S., Pociecha A., Raposeiro P. M., Room E.-I., Rotta F., Salmaso N., Sarma S. S. S., Sartirana D., Scordo F., Sibomana C., Siewert D., Stepanowska K., Tavsanoglu U. N., Tereshina M., Thompson J., Tolotti M., Valois A., Verburg P., Welsh B., Wesolek B., Weyhenmeyer G. A., Wu N., Zawisza E., Zink L., Leoni B.. Plastic debris in lakes and reservoirs. Nature. 2023;619(7969):317–322. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06168-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tang N., Yu Y., Cai L., Tan X., Zhang L., Huang Y., Li B., Peng J., Xu X.. Distribution Characteristics and Source Analysis of Microplastics in Urban Freshwater Lakes: A Case Study in Songshan Lake of Dongguan, China. Water. 2022;14(7):1111. doi: 10.3390/w14071111. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

