Artesunate Promotes Bone Remodeling Through TRAF6-Mediated NF-κB Signaling Under Orthodontic Stress in Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 40393315
- PMCID: PMC12148436
- DOI: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.04.011
Artesunate Promotes Bone Remodeling Through TRAF6-Mediated NF-κB Signaling Under Orthodontic Stress in Diabetic Rats
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the effects of artesunate (ART) on bone remodeling in vivo under orthodontic stress in diabetic rats and explore the underlying mechanisms in vitro.
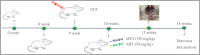
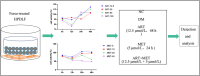
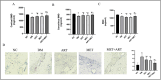
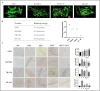
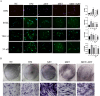
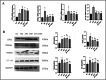
Materials and methods: A rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus with orthodontic tooth movement was established. The rats received ART and/or metformin (Met) orally. The effects of ART and Met on periodontium changes were evaluated using tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase and immunohistochemical staining. Molecular docking analyses were employed to investigate the mechanisms of ART action. In vitro, the effects of ART on osteogenic and osteoclastic activity were explored by examining TRAF6 and NF-κB expression under hyperglycemic and static pressure conditions via immunofluorescence and Western blotting.
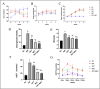
Results: ART enhanced bone metabolism despite hyperglycemia, though mechanical stress still induced bone resorption. Treatment with ART alone or in combination with Met promoted osteogenesis. TRAF6, NF-κB and the OPG/RANKL/RANK signaling pathways have been identified as key mediators of these effects. The expression of the osteogenesis-associated factor OPG increased after ART and Met treatment, while that of TRAF6 and the osteoclast-associated factors RANKL and NF-κB decreased.
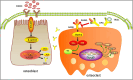
Conclusions: Increased bone resorption and decreased bone formation are characteristics of type 2 diabetes, impacting orthodontic tooth movement. ART administration alone promotes bone remodeling under static pressure and hyperglycemic conditions. These effects are mediated by lowering blood sugar levels, inhibiting osteoclast function, and improving osteogenesis through mechanisms closely associated with the OPG/TRAF6/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: Artesunate; Bone reconstruction; NF-κB; Orthodontic force; TRAF6; Type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Higham C., Abrahamsen B. Regulation of bone mass in endocrine diseases including diabetes. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;36(2):101614. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

