Chromogranin A deficiency attenuates tauopathy by altering epinephrine-alpha-adrenergic receptor signaling in PS19 mice
- PMID: 40393970
- PMCID: PMC12092710
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59682-6
Chromogranin A deficiency attenuates tauopathy by altering epinephrine-alpha-adrenergic receptor signaling in PS19 mice
Abstract
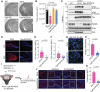
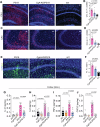
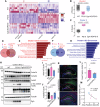
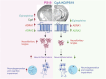
Metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance and hypertension are potential risk factors for aging and neurodegenerative diseases. These conditions are reversed in Chromogranin A (CgA) knockout (CgA-KO) mice. CgA is known to be associated with protein aggregates in the brains of neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease (AD). Here, we investigated the role of CgA in Tau pathogenesis in AD and corticobasal degeneration (CBD). CgA ablation in Tauopathy mice (PS19) (CgA-KO/PS19) reduced pathological Tau aggregation and spreading, extended lifespan, and improved cognitive function. Transcriptomic and metabolite analysis of mouse cortices revealed elevated alpha-1-adrenergic receptors (Adra1) expression and high Epinephrine (EPI) levels in PS19 mice compared to WT mice, mirroring observations in AD and CBD patients. CgA depletion in PS19 mice lowered cortical EPI levels and the expression of Adra1 back to normal. Treatment of WT hippocampal organotypic slice cultures with EPI or Adra1 agonist promoted, while an Adra1 antagonist inhibited Tau hyperphosphorylation and formation of neurofibrillary tangles, which is unaltered upon CgA depletion. These findings demonstrate the involvement of CgA in Tau pathogenesis and highlight the interplay between the EPI-Adra1 signaling pathway and CgA in Tauopathy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.K.M. is the founder of CgA Therapeuticals, Inc. GG and SKM are the founders of Siraj Therapeutics. I.L. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board for the Rossy PSP Program at the University of Toronto, Aprinoia, Amydis, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee. She receives her salary from the University of California, San Diego, and as Chief Editor of Frontiers in Neurology. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Update of
-
Chromogranin A (CgA) Deficiency Attenuates Tauopathy by Altering Epinephrine-Alpha-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 12:2024.06.11.598548. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.11.598548. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 20;16(1):4703. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59682-6. PMID: 38915622 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Chromogranin A Deficiency Attenuates Tauopathy by Altering Epinephrine-Alpha-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 9:rs.3.rs-4797912. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4797912/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 20;16(1):4703. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59682-6. PMID: 39149499 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Chromogranin A Deficiency Attenuates Tauopathy by Altering Epinephrine-Alpha-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 9:rs.3.rs-4797912. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4797912/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 20;16(1):4703. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59682-6. PMID: 39149499 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Chromogranin A (CgA) Deficiency Attenuates Tauopathy by Altering Epinephrine-Alpha-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 12:2024.06.11.598548. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.11.598548. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 20;16(1):4703. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59682-6. PMID: 38915622 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Modulation of neuronal α1-adrenergic receptor reduces tauopathy and neuroinflammation by inhibiting the STING/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway in Alzheimer's disease mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Jul 17;22(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03506-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40676669 Free PMC article.
-
Tau Interacting Proteins: Gaining Insight into the Roles of Tau in Health and Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1184:145-166. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9358-8_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 32096036 Review.
-
Tau aggregation in the hippocampal formation: an ageing or a pathological process?Exp Gerontol. 2002 Oct-Nov;37(10-11):1291-6. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(02)00141-9. Exp Gerontol. 2002. PMID: 12470843 Review.
Cited by
-
Boolean Network Modeling Identifies Cognitive Resilience in the First Murine Model of Asymptomatic Alzheimer's Disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 13:2025.06.11.659207. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.11.659207. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40661391 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Blaschko, H., Comline, R. S., Schneider, F. H., Silver, M. & Smith, A. D. Secretion of a chromaffin granule protein, chromogranin, from the adrenal gland after splanchnic stimulation. Nature215, 58–59 (1967). - PubMed
-
- Mosley, C. A. et al. Biogenesis of the secretory granule: chromogranin A coiled-coil structure results in unusual physical properties and suggests a mechanism for granule core condensation. Biochemistry46, 10999–11012 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Schober, M., Howe, P. R., Sperk, G., Fischer-Colbrie, R. & Winkler, H. An increased pool of secretory hormones and peptides in adrenal medulla of stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension13, 469–474 (1989). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 NS112010/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS100610/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS114764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026929/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG078635/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG078185/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG072487/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM085490/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI163327/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R25 NS098999/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2022-0002/Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration (AFTD)
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG063911/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG074273/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

