SKSR1 identified as key virulence factor in Cryptosporidium by genetic crossing
- PMID: 40394032
- PMCID: PMC12092579
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60088-7
SKSR1 identified as key virulence factor in Cryptosporidium by genetic crossing
Abstract
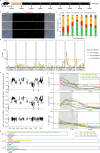
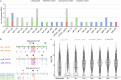
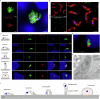
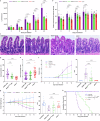
Cryptosporidium is a major cause of severe diarrhea. Although Cryptosporidium isolates exhibit significant differences in infectivity and virulence, the genetic determinants for these traits are not clear. In this study, we use classical genetics to cross two Cryptosporidium parvum isolates of different virulence and use bulk segregant analysis of whole-genome sequences from the progeny to identify quantitative trait loci (QTL) associated with Cryptosporidium infectivity and virulence. Of the 23 genes in three QTL, two have loss-of-function mutations in the low-virulence isolates, including the SKSR1 gene encoding a variant secretory protein. Deletion of the SKSR1 gene or expression of the frame-shifted sequence reduces the pathogenicity of the virulent isolate. SKSR1 is expressed in small granules and secreted into the parasite-host interface during invasion. These results demonstrate that SKSR1 is an important virulence factor in Cryptosporidium, and suggest that the extended SKSR protein family, encoded by clusters of subtelomeric genes, may contribute to pathogenesis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kotloff, K. L. et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): a prospective, case-control study. Lancet382, 209–222 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Feng, Y., Ryan, U. M. & Xiao, L. Genetic diversity and population structure of Cryptosporidium. Trends Parasitol.34, 997–1011 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32030109/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32150710530/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 31972697/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 31820103014/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 31972697/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

