Haplotype-resolved chromosome-level genome sequence of Elsholtzia splendens (Nakai ex F.Maek.)
- PMID: 40394069
- PMCID: PMC12092835
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-025-05214-2
Haplotype-resolved chromosome-level genome sequence of Elsholtzia splendens (Nakai ex F.Maek.)
Abstract
Elsholtzia splendens, a perennial herb native to East Asia, is valued for its ornamental and medicinal uses, particularly in treating inflammatory and febrile conditions. Recent studies have highlighted its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antidepressant, antithrombotic, and lipid-lowering properties of its compounds. Additionally, E. splendens shows potential for phytoremediation owing to its ability to hyperaccumulate copper (Cu), lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), and cadmium (Cd). However, its role in remediation conflicts with its medicinal use because of the risk of heavy metal accumulation. Genome sequencing will be key to boosting beneficial compound production and reducing heavy metal risks. In this study, we generated a high-resolution, haplotype-resolved, chromosome-scale genome sequence of E. splendens using PacBio Revio long-read, Illumina short-read, and Hi-C sequencing technologies. The haplotype genome assemblies, spanned 275.4 and 265.0 Mbp with a scaffold N50 of 33.9 and 33.8 Mbp for haplotype 1 and 2, respectively. This assembly provides valuable insights into medicinal compound biosynthesis and supports genetic conservation efforts, facilitating future genetic and biotechnological applications of E. splendens for medicinal and ecological uses.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

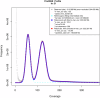
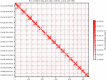
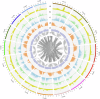
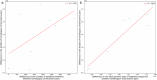
References
-
- Plants of the World Online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published on the Internet edn (2024).
-
- Kim, W. S. & Lim, Y. Antithrombotic Activity of Extracts from the Aromatic Herb Elsholtzia splendens. Biomedical Science Letters23, 277–280 (2017). - DOI
-
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for the Western Pacific. Medicinal plants in the Republic of Korea: information on 150 commonly used medicinal plants, (WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific, Manila, 1998).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

