Identification of oncogenes associated with colorectal cancer mortality and the effect of cinnamon-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles on their expression
- PMID: 40394097
- PMCID: PMC12092824
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-02189-3
Identification of oncogenes associated with colorectal cancer mortality and the effect of cinnamon-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles on their expression
Abstract
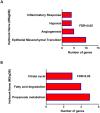
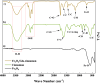
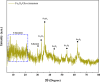
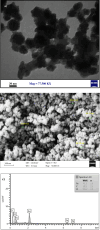
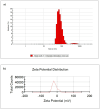
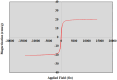
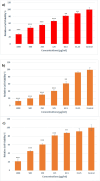
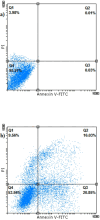
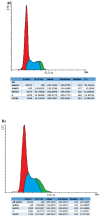
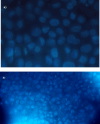
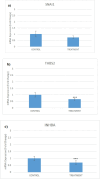
Finding the molecular targets involved in the severity and drug resistance of Colorectal cancer (CRC) and applying targeted treatments against them is a promising approach. In this study, some candidate oncogenes related to disease severity and mortality were identified by extracting bioinformatics data, and the effect of Fe3O4@Glu-Cinnamon NPs on the survival of CRC cells (SW480) and the expression of these oncogenes was investigated. The NPs were characterized by FT-IR, XRD, DLS and zeta potential measurement, TEM and SEM imaging, EDS-mapping and VSM analysis. Cytotoxicity of the NPs was evaluated by the MTT assay and a flow cytometry analysis was done to investigate cell apoptosis/necrosis levels and cell cycle analysis of cancer cells. The Fe3O4@Glu-Cinnamon NPs with spherical morphology were correctly synthesized, containing no elemental impurities, with a size range of 26.8-60.2 nm, DLS of 213 nm, zeta potential of -15.4mV and maximum magnetization level of 20.33emu/g. Treatment of cancer cells with the NPs elevated primary and late apoptosis and cell necrosis levels to 20.85, 16.83 and 9.56% and treated cells were mainly arrested at the S and G2/M phases. The expression level of the oncogenes associated with mortality, SNAI1, THBS2 and INHBA reduced to 0.74, 0.66 and 0.7 folds, respectively. The magnetic properties of Fe3O4 NPs enable their potential use in targeted drug delivery, allowing for site-specific accumulation within tumors. This could minimize systemic toxicity while enhancing treatment efficacy.
Keywords: Cinnamon; Colorectal cancer; Iron oxide nanoparticles; Oncogene.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Iron oxide nanoparticles coated with Glucose and conjugated with Safranal (Fe3O4@Glu-Safranal NPs) inducing apoptosis in liver cancer cell line (HepG2).BMC Chem. 2024 Feb 15;18(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01142-1. BMC Chem. 2024. PMID: 38360669 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Fe3O4@Glu-Oleuropein Nanoparticles in Targeting KRAS Pathway-Regulating lncRNAs in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 Jul;202(7):3073-3085. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03892-w. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 37792268
-
Antibacterial potential and cytotoxic activity of iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with thymol (Fe3O4@Glu-Thymol) on breast cancer cells and investigating the expression of BAX, CASP8, and BCL-2 genes.Biometals. 2023 Dec;36(6):1273-1284. doi: 10.1007/s10534-023-00516-7. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Biometals. 2023. PMID: 37351759
-
Evaluation the cytotoxic effect of Fe3O4@Glu-Gingerol on lung adenocarcinoma cell line (A549) with biological mechanisms.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 10;10(1):e23419. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23419. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38173472 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin loaded magnetic Fe3O4/carboxymethylchitosan nanoparticles as tumor-targeted drug delivery system: Synthesis and in vitro characterization.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015 Apr 1;128:379-388. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.02.035. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015. PMID: 25779605
Cited by
-
Integrative single-cell transcriptomic analysis deciphers heterogeneous characteristics of gastrointestinal tract cancer.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Aug;15(8):e70415. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70415. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40785647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung, H. et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J. Clin.71 (3), 209–249. 10.3322/caac.21660 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Favoriti, P. et al. Worldwide burden of colorectal cancer: a review. Updates Surg.68, 7–11. 10.1007/s13304-016-0359-y (2016). - PubMed
-
- Hu, J. et al. Magnetically active Fe 3 O 4 nanorods loaded with tissue plasminogen activator for enhanced thrombolysis. Nano Res.9, 2652–2661. 10.1007/s12274-016-1152-4 (2016).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

