Matrix Remodeling Associated Genes (MXRAs): structural diversity, functional significance, and therapeutic potential in tumor microenvironments
- PMID: 40394417
- PMCID: PMC12092922
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02728-4
Matrix Remodeling Associated Genes (MXRAs): structural diversity, functional significance, and therapeutic potential in tumor microenvironments
Abstract
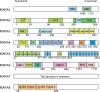
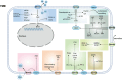
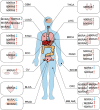
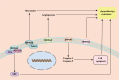
The Matrix Remodeling Associated Genes (MXRAs) family, comprising eight distinct members (MXRA1-8), plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of higher vertebrate cells. These proteins are primarily involved in the regulation of intercellular adhesion and the remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Recent investigations have highlighted the significant roles of MXRAs in the modulation of tumor growth and progression, establishing them as vital components in the oncogenic landscape. Notably, each MXRA member exhibits unique structural characteristics and functional properties, contributing to a diverse array of regulatory effects within the tumor context. This review seeks to provide a comprehensive analysis of the structural attributes, functional contributions, and activities of MXRAs within the tumor microenvironment. By elucidating the underlying mechanisms of action, this paper aims to offer novel insights and strategic approaches for the identification of early diagnostic biomarkers, as well as potential therapeutic targets that may facilitate molecular interventions aimed at inhibiting tumor development.
Keywords: Cell adhesion; MXRAs; Matrix remodeling; Tumor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study does not involve ethical issues. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The regulatory roles of T helper cells in distinct extracellular matrix characterization in breast cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 8;13:871742. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.871742. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36159822 Free PMC article.
-
The role of tenascin-C in tumor microenvironments and its potential as a therapeutic target.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Feb 19;13:1554312. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1554312. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40046232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular Extracellular Matrix Remodeling and Hypertension.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021 Apr 1;34(10):765-783. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8110. Epub 2020 May 27. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021. PMID: 32460598 Review.
-
The matrix environmental and cell mechanical properties regulate cell migration and contribute to the invasive phenotype of cancer cells.Rep Prog Phys. 2019 Jun;82(6):064602. doi: 10.1088/1361-6633/ab1628. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Rep Prog Phys. 2019. PMID: 30947151 Review.
-
Tumor Extracellular Matrix Remodeling: New Perspectives as a Circulating Tool in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Solid Tumors.Cells. 2019 Jan 23;8(2):81. doi: 10.3390/cells8020081. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30678058 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lafrenie RM, Buckner CA, Bewick MA. Cell adhesion and cancer: is there a potential for therapeutic intervention? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007;11(6):727–31. 10.1517/14728222.11.6.727. - PubMed
-
- Mohan V, Das A, Sagi I. Emerging roles of ECM remodeling processes in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;62:192–200. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.09.004. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
