Dysfunctional mesocorticolimbic circuitry in cluster headache
- PMID: 40394469
- PMCID: PMC12090487
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-025-02017-z
Dysfunctional mesocorticolimbic circuitry in cluster headache
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to identify mesocorticolimbic functional abnormalities in cluster headache (CH) patients, disentangling the roles of chronification and affective symptoms.
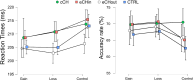
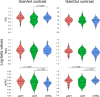
Methods: Using the monetary incentive delay fMRI task to directly engage these pathways, we investigated functional alterations in key regions of this network in chronic (n = 23) and episodic CH patients (n = 49) compared to a control group (n = 32). After processing the fMRI data, we extracted beta values from selected regions and for contrasts of interest and entered them into logistic regression models adjusted for potential confounders (such as depressive and anxiety symptoms and smoking habit) to test their association with the diagnoses (chronic CH and control subjects, episodic CH and control subjects).
Results: Results showed that chronic CH patients exhibited reduced ventral tegmental area (VTA) activity and a tendency towards significance (p = 0.056) for an increased medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) responsiveness during reward anticipation, alongside a significant decrease in mPFC activity during reward outcomes. Episodic patients displayed abnormal mPFC activity across both reward phases, but coupled with intact VTA responses. Importantly, these functional abnormalities were not correlated to depressive and anxiety symptoms and smoking habits.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that chronic CH patients experience an imbalance in the VTA-mPFC pathway, while episodic patients may show early signs of this emerging dysfunction. Moreover, the observed reward processing alterations seem distinct from those associated with affective disorders, possibly highlighting unique mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of CH.
Keywords: Chronic cluster headache; Episodic cluster headache; Medial prefrontal cortex; Mesocorticolimbic system; Monetary incentive delay task; Nucleus accumbens; Ventral tegmental area; fMRI.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The Authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abagnale C, Di Renzo A, Giuliani G, Sebastianelli G, Casillo F, Ziccardi L, Parisi V, Di Lorenzo C, Serrao M, Caramia F (2025) others. MRI-based analysis of the microstructure of the thalamus and hypothalamus and functional connectivity between cortical networks in episodic cluster headache. J Headache Pain 26:12 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- M112022YFWZ0003/Key Research and Development Program of Sichuan Province
- M112022YFWZ0003/Key Research and Development Program of Sichuan Province
- M112022YFWZ0003/Key Research and Development Program of Sichuan Province
- M112022YFWZ0003/Key Research and Development Program of Sichuan Province
- RF-2016-02364909/Italian Ministry of Health
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

