Identification and prioritization of population health indices in Iranian population, a qualitative study
- PMID: 40394529
- PMCID: PMC12090397
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-22985-w
Identification and prioritization of population health indices in Iranian population, a qualitative study
Abstract
Introduction: A population health index is a combination of two or more health indicators, used to evaluate different dimensions of health in a population. While various population health indices have been developed globally, there remains a gap in systematically identifying and prioritizing such indices tailored to the Iranian context. This study aims to identify and prioritize population health indices relevant to the Iranian context using expert consensus through the Delphi method.
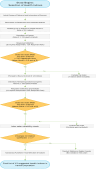
Methodology: A multi-methodology with two steps was employed in this study. Firstly, a comprehensive list of existing composite health indicators was identified by reviewing the literature. In the second stage, the review results were used as input for a web-based Delphi survey involving 22 experts across two rounds. After two rounds, a list of indices that gained at least 70% of consensus and a mean score of 2.5 out of 5 was prepared.
Results: In the initial phase of the study, a refined set of 21 indices emerged. Participation rates for the first and second rounds were 72% and 68%, respectively. A total of 21 indices were assessed, and after refining them based on expert feedback, the following five indices were determined to have the highest priority after two rounds: Disability-Adjusted Life Year (4.23 ± 0.32), UHC Service Coverage index (3.96 ± 0.25), Sustainable Development Goals index (3.78 ± 0.31), Human Development Index (3.58 ± 0.36), Quality-Adjusted Life Year (3.58 ± 0.37). The Inter-rater reliability test found significant absolute agreement among experts in the second round (ICC: 0.970, 95% CI: 0.931-0.989).
Conclusion: This study's contribution lies in offering a compilation of composite health indicators, which can guide forthcoming research on the health measurement of the Iranian population. Furthermore, the study underscores the value of involving expert professionals and soliciting diverse perspectives in selecting health indices.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Iran University of Medical Sciences. (Ethical code: IR.IUMS.FMD.REC.1399.454). Informed consent was obtained from all participants, and their anonymity was maintained throughout the study. Participants were also informed that their opinions would be confidential. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Indicators for evaluating European population health: a Delphi selection process.BMC Public Health. 2018 Apr 27;18(1):557. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5463-0. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29703176 Free PMC article.
-
Key indicators for appraising adolescent sexual and reproductive health in South Asia: international expert consensus exercise using the Delphi technique.Glob Health Action. 2020 Dec 31;13(1):1830555. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2020.1830555. Glob Health Action. 2020. PMID: 33076781 Free PMC article.
-
360-degree Delphi: addressing sociotechnical challenges of healthcare IT.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020 Jun 5;20(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12911-020-1071-x. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020. PMID: 32503609 Free PMC article.
-
Policy options to address the effectiveness of health service management graduates in solving Iranian health system challenges: a mixed scoping review and policy Delphi approach.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Oct 5;77:102875. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102875. eCollection 2024 Nov. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39430615 Free PMC article.
-
Indicators of outcome quality in peripheral arterial disease revascularisations - a Delphi expert consensus.Vasa. 2018 Oct;47(6):491-497. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000720. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Vasa. 2018. PMID: 29856270 Review.
References
-
- Organization WH. Support tool to strengthen health information systems: guidance for health information system assessment and strategy development. 2021.
-
- Kaltenthaler E, Maheswaran R, Beverley C. Population-based health indexes: a systematic review. Health Policy. 2004;68(2):245–55. - PubMed
-
- Etches V, Frank J, Ruggiero ED, Manuel D, MEASURING. POPULATION HEALTH: A Review of Indicators. 2006;27(1):29–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous