The effect of shared decision-making on the conflict and regret in menopause symptoms management: an interventional study
- PMID: 40394544
- PMCID: PMC12090383
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-025-03774-4
The effect of shared decision-making on the conflict and regret in menopause symptoms management: an interventional study
Abstract
Introduction: Menopausal women often face challenges in choosing appropriate interventions to mitigate distressing menopause symptoms, primarily due to concerns about treatment suitability. Therefore, the present study aimed to assess the effect of shared decision-making (SDM) on conflict and regret in menopause symptoms management.
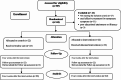
Method: This interventional study was conducted on 44 menopausal women aged ≥ 45 years in Tabriz, Iran, from September 2020 to January 2021. Subjects were randomly assigned to the intervention (n = 22), which received SDM-based counseling along with a decision aid (DA) booklet, and control (n = 22) groups. The data were collected using a socio-demographic and obstetric characteristics checklist, awareness of the menopause symptoms management strategies, decisional conflict, and regret. The intergroup differences were compared employing an independent t-test and ANCOVA.
Results: The mean score of decision conflict [Mean difference (MD): -2.07, 95% CI: -29.65 to -11.92, P = 0.001] and decision regret [MD: -1.25, 95% CI: -1.64 to 0.64, P = 0.03] significantly reduced in the intervention group compared to the control group after the intervention. Additionally, a statistically significant increase in the mean score of women's awareness was observed in the intervention group compared to the control group following the intervention [(Hormone Therapy: MD: 3.38, 95% CI: 1.01 to 5.57, P = 0.006) (Natural Products: MD: 2.44, 95% CI: 0.93 to 3.94, P = 0.002)].
Conclusion: The results indicated the effect of SDM-based counseling on improving women's awareness of the menopause symptoms management strategies and reducing the decisional conflict and regret.
Keywords: Awareness; Decision regret; Decisional conflict; Postmenopausal symptoms; Shared decision-making.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Deputy of Research and Technology of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences (ethical code: IR.TBZMED.REC.1399.244). Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants who participated in the study. In addition, all methods are done in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
References
-
- Hakimi S, Nazarpour S, RAMEZANI TF, Simbar M, Zaiery F. Women’s experiences about menopause and related factors. 2017, URL: http://ijem.sbmu.ac.ir/article-1-2250-en.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical