Improving nurse's knowledge, attitudes, and skills in lactation and breastfeeding management using a blended learning approach: a quasi-experimental study
- PMID: 40394548
- PMCID: PMC12093762
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-025-07341-1
Improving nurse's knowledge, attitudes, and skills in lactation and breastfeeding management using a blended learning approach: a quasi-experimental study
Abstract
Background: Breastfeeding is crucial for newborn health; however, India faces unique challenges in promoting breastfeeding. Nurses play a vital role in supporting breastfeeding, and their knowledge, attitudes, and skills are essential. This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of a blended learning approach in improving nurses' competencies in lactation and breastfeeding management.
Methods: A quasi-experimental, one-group pre-test and post-test study was conducted with 129 newly appointed nurses at a tertiary care center in India. The intervention was a week-long blended learning program that included self-study materials, interactive sessions, and hands-on practice. Nurses' knowledge, attitudes, and skills were assessed before, immediately after, and three months post-intervention using structured questionnaires and observation checklists.
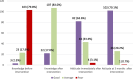
Results: Nurses' knowledge scores significantly improved immediately post-intervention (24.7 ± 3.8) and were sustained at three months (24.2 ± 3.6) compared to pre-intervention (17.5 ± 4.9) (p < .001). The majority of nurses demonstrated a good attitude post-intervention (63.6%), which further increased at three months (79.1%). Skill scores related to positioning and attachment, management of breast problems, manual expression of milk, paladai feeding, and orogastric tube feeding significantly improved post-intervention and were maintained at three months after the intervention.
Conclusions: The blended learning approach effectively improved nurses' knowledge, attitudes, and skills in lactation and breastfeeding management, with sustained competencies at three months post intervention. Implementing regular training programs and incorporating lactation education into nursing curricula can enhance nurses' capacity to support optimal breastfeeding. Future studies should explore the impact of these interventions on patient outcomes.
Keywords: Attitude; Blended learning; Breastfeeding management; Knowledge; Lactation; Nurses; Skills.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Institutional Ethics Committee of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Kalyani, reviewed and approved the study (IEC/AIIMS/Kalyani/Meeting/2022/25). Written informed consent was obtained from all the eligible participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yadav S, Ahmad S, Lohani P, Gahlot A, Kumar M. Exploring breastfeeding practices and influencing factors among the KOL tribe in Uttar Pradesh: a mixed-methods study. Indian J Community Health. 2024;36:538–48. - DOI
-
- Bharati P, Pal M, Bandyopadhyay M, Bhakta A, Chakraborty S, Bharati P. Prevalence and causes of low birth weight in India. Malays J Nutr. 2011;17:301–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical