Efficacy of topical mesenchymal stem cell exosome in Sjögren's syndrome-related dry eye: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 40394561
- PMCID: PMC12090426
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-025-04078-9
Efficacy of topical mesenchymal stem cell exosome in Sjögren's syndrome-related dry eye: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
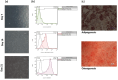
Background: Sjögren's syndrome (SS) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder affecting salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to distressing ocular symptoms. Existing therapeutic approaches for SS-associated dry eye syndrome (DES) show insufficient efficacy. This study investigates the use of topical MSC-derived exosomes in primary SS-related DES.
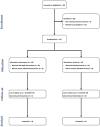
Methods: In phase 1 and 2, triple-blinded, randomized trial, two vials of eye drops are given to each participant, one with code A and one with code B and only the supervisor knows the content of each vial. The treatment group (n = 8 eyes) received 10 µg of MSC-derived exosomes twice daily for two weeks and the control group (n = 8 eyes) received Phosphate buffered saline(PBS) for their respective eyes. Safety was assessed through ophthalmic exams, while DES assessment tests evaluated treatment effectiveness. Non-parametric tests employed to examine assumptions. The differences of ocular examination results between day 0 and month 3 were analyzed using a paired Student's t test. Measurement data that were not normally distributed are represented by the median (interquartile range), and comparisons were performed using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
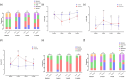
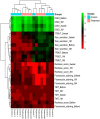
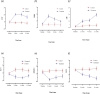
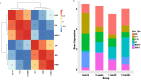
Results: The treatment showed promising results, with significant improvements observed in various indicators such as reduced Ocular Surface Disease Index scores, increased tear secretion, lower fluorescein scores, and longer tear-film break-up time before and after treatment and between the controls and the treated groups. Our results showed a significant increase in multifunctional proteins such as Epidermal Growth Factor and thrombospondin-1 and conversely, the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6 and Matrix metalloproteinase-9 significantly decreased in tear of participant before and after treatment and between the controls and the treated groups.
Conclusions: Our study underscores the safety and substantial therapeutic potential of using MSC-derived extracellular exosomes eye drops to treat SS-associated DES.
Trial registration: IRCT20211102052948N1 The study protocol has been approved in Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials at 2022-04-20.
Keywords: Dry eye; Exosomes; Mesenchymal stem cell; Sjögren's syndrome.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participants: Before their inclusion in the study, written informed consent was obtained from the WJ tissue donors and participants with SS. The trial was conducted in accordance with the guidelines for conducting clinical trials on human participants and the Declaration of Helsinki. Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Ethics Committee, Shiraz, Iran, approved the study protocol (IR.SUMS.REC.1400.852). The study protocol was also registered in the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (IRCT20211102052948N1) at 2022-04-20. Consent for publication: Before the participant enters the study, written informed consent was obtained from WJ tissue donors and SS participants for the publication of results that will be used in a completely confidential manner and solely for research purposes, and the participants’ identity will remain confidential within the framework of the law. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Li D-Q, et al. Hyperosmolarity stimulates production of MMP-9, IL-1ß and TNF- by human corneal epithelial cells via a c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway. Volume 43. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science; 2002. pp. 1981–1981. 13.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

