YY1-induced DDX18 modulates EMT via the AKT/mTOR pathway in esophageal cancer: a novel therapeutic target
- PMID: 40394670
- PMCID: PMC12090415
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06555-7
YY1-induced DDX18 modulates EMT via the AKT/mTOR pathway in esophageal cancer: a novel therapeutic target
Abstract
Background: Esophageal cancer is the 11th most common malignancy and the 7th leading cause of cancer-related death globally. Identifying key molecules and underlying mechanisms in the progression of esophageal cancer represents an effective strategy for developing novel therapeutic approaches.
Methods: DDX18 expression in clinical specimens was evaluated by immunohistochemistry and western blot analysis. Functional assays were performed in cells with either DDX18 knockdown or overexpression. Dual luciferase reporter assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) were conducted to validate the interaction between YY1 and the DDX18 promoter. A xenograft tumor model was utilized to investigate the role of DDX18 in vivo in esophageal cancer.
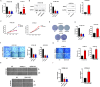
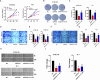
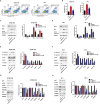
Results: DDX18 was found to be markedly overexpressed in esophageal cancer, with its levels significantly higher in patients with pathological grade III compared to those with grades I-II. In vitro, DDX18 enhanced cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, while concurrently suppressing apoptosis. Furthermore, DDX18 promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and activated the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. The use of AKT inhibitors effectively abrogated the oncogenic effects of DDX18. Dual luciferase and ChIP assays confirmed that YY1 binds to and stimulates DDX18 transcription. In rescue experiments, YY1 countered the inhibitory effects of DDX18 knockdown on cell proliferation, EMT, and AKT/mTOR activation. In vivo, DDX18 knockdown resulted in reduced tumor growth.
Conclusions: The transcription of DDX18 was activated by YY1, and DDX18 promoted tumor cell growth and EMT through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in esophageal cancer cells.
Keywords: DDX18; Apoptosis; EMT; Esophageal cancer; Transcription factor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This research study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of The First Hospital of Jilin University. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Annexin A2 combined with TTK accelerates esophageal cancer progression via the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Apr 24;15(4):291. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06683-w. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38658569 Free PMC article.
-
ENAH transcriptionally activated by YY1 promotes growth and invasion of laryngocarcinoma cells through PI3K/AKT signaling.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 15;983:176991. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176991. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39265883
-
TGIF1 plays a carcinogenic role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through the Wnt/β‑catenin and Akt/mTOR signaling pathways.Int J Mol Med. 2021 May;47(5):77. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4910. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Int J Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33693954 Free PMC article.
-
NDRG2 suppresses proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of esophageal cancer cells through regulating the AKT/XIAP signaling pathway.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Jun;99:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29530788
-
MiR-206 inhibits HGF-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer via c-Met /PI3k/Akt/mTOR pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 5;7(14):18247-61. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7570. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26919096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries [J]. Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. - PubMed
-
- Eisner D C. Esophageal cancer: treatment advances and need for screening [J]. Jaapa. 2024;37(4):19–24. - PubMed
-
- Deboever N, Jones C M, Yamashita K, et al. Advances in diagnosis and management of cancer of the esophagus [J]. BMJ. 2024;385:e074962. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

