Altered activity within the social behavior neural network in adolescent rats following prenatal alcohol exposure and/or early-life adversity
- PMID: 40395053
- PMCID: PMC12285919
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.70082
Altered activity within the social behavior neural network in adolescent rats following prenatal alcohol exposure and/or early-life adversity
Abstract
Background: Social behavior relies on the dynamic, complex, and coordinated activity of a highly conserved "social behavior neural network," which includes the olfactory bulb (OB), piriform cortex (PCX), lateral septum, medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), amygdala, paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN), and ventral hippocampus. Prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) is known to disrupt social behavior development, leading to lifelong social functioning impairments. Individuals with PAE are at heightened risk of experiencing early-life adversity (ELA), which independently affects social behavior development; however, little is known about the combined effects of PAE and ELA on social behavior.
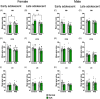
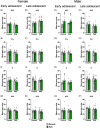
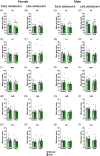
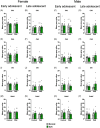
Methods: We previously demonstrated that PAE and ELA impact social recognition memory throughout adolescence; here, we combine animal models of PAE and ELA to gain insight into both independent and interactive effects of these insults on social behavior network neural activity in both early and late adolescent male and female rats. We measured neural activity (c-fos mRNA expression) across the network following social recognition memory testing.
Results: Our findings indicate that both PAE and ELA are associated with altered neural activity in regions supporting social recognition memory, notably the OB, PCX, mPFC, amygdala, and PVN. The direction of these effects and specific regions impacted vary by sex and age at assessment. Importantly, different brain areas exhibit distinct sensitivities to each type of insult, with PAE generally resulting in hypoactivity of the amygdala and ELA altering mPFC activity.
Conclusions: These data contribute to a more complete social neurobehavioral profile, accounting for both PAE and ELA, to support earlier diagnoses and interventions.
Keywords: c‐fos; adolescence; early‐life adversity; neural activity; prenatal alcohol exposure; social behavior neural network.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alcohol, Clinical and Experimental Research published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Research Society on Alcohol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and Transient Systemic Hypoxia-Ischemia Result in Subtle Alterations in Dendritic Complexity in Medial Frontal Cortical Neurons in Juvenile and Young Adult Rat Offspring in a Pilot Study.Cells. 2024 Nov 30;13(23):1983. doi: 10.3390/cells13231983. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39682731 Free PMC article.
-
Peripuberty Is a Sensitive Period for Prefrontal Parvalbumin Interneuron Activity to Impact Adult Cognitive Flexibility.Dev Neurosci. 2025;47(2):127-138. doi: 10.1159/000539584. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Dev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 38830346 Free PMC article.
-
Oral and written communication skills of adolescents with prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) compared with those with no/low PAE: A systematic review.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2021 Jul;56(4):694-718. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12644. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2021. PMID: 34137136 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of Methamphetamine Exposure during Adolescence Differentially Influences Parvalbumin and Perineuronal Net Immunoreactivity in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex of Female, but Not Male, Rats.Dev Neurosci. 2025;47(1):27-39. doi: 10.1159/000538608. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Dev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 38547851 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions for adults who have sexually offended or are at risk of offending.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD007507. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007507.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adolphs, R. (2001) The neurobiology of social cognition. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 11(2), 231–239. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs, R. (2003) Cognitive neuroscience of human social behaviour. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 4(3), 165–178. - PubMed
-
- Albers, H.E. (2012) The regulation of social recognition, social communication and aggression: vasopressin in the social behavior neural network. Hormones and Behavior, 61(3), 283–292. - PubMed
-
- Althammer, F. & Grinevich, V. (2018) Diversity of oxytocin neurons: beyond magno‐ and parvocellular cell types? Journal of Neuroendocrinology, 30(8), 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Amaral, D.G. (2003) The amygdala, social behavior, and danger detection. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1000(1), 337–347. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

