Trends in Research on the P2X7 Receptor: A Bibliometric and Visualization Analysis
- PMID: 40395554
- PMCID: PMC12091240
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S522380
Trends in Research on the P2X7 Receptor: A Bibliometric and Visualization Analysis
Abstract
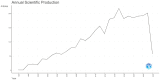
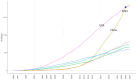
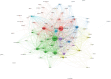
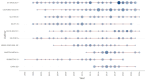
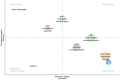
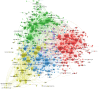
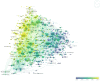
The P2X7 receptor (P2X7R), activated by ATP, participates in mediating a variety of biological processes such as the release of inflammatory factors, thereby affecting the pathogenesis of numerous diseases. Despite its clinical significance, comprehensive bibliometric studies on P2X7R-related research remain scarce. To address this gap, we conducted a bibliometric investigation to quantify publication outputs, identify leading contributors, and map geographical distributions of P2X7R-related research, ultimately elucidating current research frontiers and emerging trends. Utilizing visualization techniques, complex bibliometric relationships were transformed into interpretable graphical representations. Our Web of Science query for "P2X7R" identified 4551 original research articles by 13,471 authors published since 1985. Publication volume demonstrated sustained growth, with China emerging as the predominant contributor in quantitative output (1871 articles) and the United States leading in international collaborations. Thematic mapping revealed two principal research areas: "P2X7R, inflammation, microglia" and "P2X7R, apoptosis, purinergic". Notably, "P2X7R, P2 receptors, oxidative stress" encompassed both motor and niche themes, thus representing the trajectory of future development potential. Through bibliometric and visualization analysis, we found that the literature related to P2X7R is on the rise and will enter a new stage of interdisciplinary integration development in the future.
Keywords: P2X7 receptor; VOSviewer; bibliometrix; web of science.
© 2025 Ren et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
P2X7 receptors: a bibliometric review from 2002 to 2023.Purinergic Signal. 2024 Feb 29. doi: 10.1007/s11302-024-09996-9. Online ahead of print. Purinergic Signal. 2024. PMID: 38421486 Review.
-
Bibliometric analysis of laryngeal cancer treatment literature (2003-2023).Heliyon. 2024 Dec 16;11(1):e40832. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40832. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39811326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Hotspots and Development Trends on Apolipoprotein B in the Field of Atherosclerosis: A Bibliometric Analysis.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun;67(6):2204-2222. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01218-2. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38963531 Review.
-
Research hotspots and trends of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for drug delivery: a bibliometric and visualization analysis from 2013 to 2023.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 30;12:1412363. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1412363. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39539963 Free PMC article.
-
Global research progress of endothelial cells and ALI/ARDS: a bibliometric analysis.Front Physiol. 2024 May 7;15:1326392. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1326392. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38774649 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

