Statins for primary prevention of cardiovascular events in people with HIV: target trial and modelling study
- PMID: 40395649
- PMCID: PMC12090529
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjmed-2024-001132
Statins for primary prevention of cardiovascular events in people with HIV: target trial and modelling study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Statins for primary prevention of cardiovascular events in people with HIV: target trial and modelling study.BMJ Med. 2025 Jul 7;4(1):e001132corr1. doi: 10.1136/bmjmed-2024-001132corr1. eCollection 2025. BMJ Med. 2025. PMID: 40735510 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness and benefit-harm balance of various statins for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in people with HIV.
Design: Target trial and modelling study.
Setting: North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD), 1995 to 2019. NA-ACCORD integrates individual level data from >20 HIV cohorts across the US and Canada from people with HIV who have successfully linked into care.
Participants: 157 699 people with HIV enrolled in one of the cohorts of NA-ACCORD. 54 165 eligible individuals, aged 40-75 years, were enrolled in the target trial.
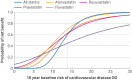
Main outcome measures: The primary outcomes for the target trial were the 10 year effects of statins on cardiovascular disease events (fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction, hospital admission for unstable angina, coronary or arterial revascularisation, fatal and non-fatal stroke, or transient ischaemic attack) and harm outcomes (type 2 diabetes, mild cognitive impairment, rhabdomyolysis, and myopathy). The secondary outcome was the 10 year risk threshold where the reduction in cardiovascular disease outweighed the increased risk of harm outcomes, showing an overall net benefit of statins.
Results: Participants who first started receiving treatment with statins (statin initiators) had a 21% reduction in cardiovascular disease events (hazard ratio 0.79, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.72 to 0.87) and a 26% reduction in the combined risk of stroke and myocardial infarction (0.74, 0.56 to 0.98), but a 12% increase in the risk of type 2 diabetes (1.12, 1.01 to 1.25) compared with participants who developed the indication but did not take statins (non-initiators). The effects on cognitive impairment (hazard ratio 1.13, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.56), myopathy (1.10, 0.76 to 1.61), and rhabdomyolysis (1.09, 0.68 to 1.75) were not statistically significant. On average, the benefit of statins exceeded harms for individuals with a 10 year baseline risk of cardiovascular disease of ≥13.8%. Subgroup specific thresholds included men (14.2%), women (11.1%), ages 40-64 years (13.8%) versus 65-75 years (15.1%), and CD4 count >200 cells/mm³ (13.6%) versus <200 cells/mm³ (15.3%). Varying weights for cardiovascular disease yielded thresholds ranging from 11.6% to 54.0%, whereas weights for harm outcomes resulted in thresholds ranging from 5.0% to >30.0%.
Conclusions: In this study, statins benefitted individuals with HIV with a moderate or high risk of cardiovascular disease, but the threshold for net benefit varied by patient subgroup and preference, implying the need to customise statin treatment to individual risks, preferences, and treatment goals. Given the limitations of observational data, further controlled studies are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of statins in people with HIV receiving modern antiretroviral therapy.
Keywords: Cardiology; Hiv; Preventive medicine.
Copyright © Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the ICMJE unifform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/disclosure-of-interest/ and declare: support from Swiss National Science Foundation, National Institutes of Health (NIH), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Health Resources and Services Administration, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), National Cancer Institute (NCI), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), National Institute for Mental Health (NIMH), National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), National Institute on Aging (NIA), National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR), National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), National Institute of Nursing Research (NINR), National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. (NIDCD), and National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) for the submitted work; funds from Merck Foundation, Gilead Sciences, ViiV Healthcare, Johnson and Johnson, Janssen, GSK and Novartis, Eli Lilly, Med-IQ, Bayer, NIH/NIAID, and TrioHealth that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; Coursera (five course specialisation), TrioHealth (advisory board), and NIH (consultation) that could appear to have influenced the submitted work; no financial relationships with any other organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Neesgaard B, Greenberg L, Miró JM, et al. Associations between integrase strand-transfer inhibitors and cardiovascular disease in people living with HIV: a multicentre prospective study from the RESPOND cohort consortium. Lancet HIV. 2022;9:e474–85. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(22)00094-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kileel EM, Malvestutto CD, Lo J, et al. Changes in Body Mass Index with Longer-term Integrase Inhibitor Use: A Longitudinal Analysis of Data from the Randomized Trial to Prevent Vascular Events in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (REPRIEVE) Clin Infect Dis. 2023;76:2010–3. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciad107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- R01 DA011602/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 EY013707/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 CP010176/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007583/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146192/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA020790/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000421/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI131895/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA037788/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA016893/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CP001004/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146333/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI124794/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA000432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA036935/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007587/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI067039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008057/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146193/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008052/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI110527/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI093197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI118591/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI065298/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA013566/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP055504/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000083/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146204/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146240/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG053100/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008067/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AA020794/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146203/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
