Gut microbiota: a new target for the prevention and treatment of insomnia using Chinese herbal medicines and their active components
- PMID: 40395724
- PMCID: PMC12088967
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1572007
Gut microbiota: a new target for the prevention and treatment of insomnia using Chinese herbal medicines and their active components
Abstract
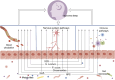
The emergence of the microbiota-gut-brain axis has opened new avenues for improving sleep quality. Recent studies have revealed a close relationship between insomnia and the gut microbiome. Chinese herbal medicines and their active components can alter the relative abundance of sleep-related gut microbiota by reversing dysbiosis in the gut microbiome. Improving sleep quality through the regulation of the gut microbiota using herbal medicine and its active components has become a highly promising therapeutic strategy. This article elucidates how the gut microbiota modulates sleep quality via the intricate communication network of the gut-brain axis. It also reviews the latest research on utilizing herbal medicine and its active components to regulate the gut microbiota for enhancing sleep quality. Additionally, it provides insights into the potential of herbal medicine and its active components in improving sleep quality through the modulation of the gut microbiota.
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicines and their active components; Gut Microbiota; improving sleep quality; insomnia; microbiota-gutbrain axis.
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Dou, Song, Yang, Liu, Song and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aghelan Z., Pashaee S., Abtahi S. H., Karima S., Khazaie H., Ezati M., et al. (2023). Natural immunosuppressants as a treatment for chronic insomnia targeting the inflammatory response induced by NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β Axis activation: a scooping review. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 18 (3), 294–309. 10.1007/s11481-023-10078-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Álvarez S. A., Rocha-Guzmán N. E., González-Laredo R. F., Gallegos-Infante J. A., Moreno-Jiménez M. R., Bravo-Muñoz M. (2022). Ancestral food sources rich in polyphenols, their metabolism, and the potential influence of gut microbiota in the management of depression and anxiety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70 (4), 944–956. 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c06151 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

