Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using E. cardamomum and zinc nitrate precursor: a dual-functional material for water purification and antibacterial applications
- PMID: 40395799
- PMCID: PMC12090044
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra01469g
Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using E. cardamomum and zinc nitrate precursor: a dual-functional material for water purification and antibacterial applications
Abstract
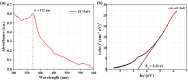
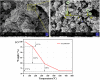
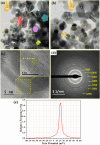
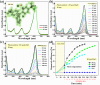
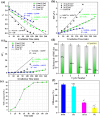
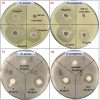
This study presents an eco-friendly, bio-engineered approach for synthesizing zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using Elettaria cardamomum pod (EC-pod) extract, offering a sustainable alternative for environmental remediation and antimicrobial applications. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis confirms the wurtzite crystalline phase, with an average particle size of 20.87 nm. Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy reveals a characteristic absorption peak at 372 nm, corresponding to an energy band gap of 3.33 eV. Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy highlights the role of phytochemicals as capping and stabilizing agents. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) confirm multi-architectural morphologies, including hexagonal, spherical, rod-like, and pentagonal structures, with energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy verifying elemental purity. The photocatalytic efficiency of EC-pod:ZnO in degrading malachite green (MG) dye under UV irradiation reaches 99.8% removal within 160 minutes, with a high quantum yield of 2.73 × 10-3 molecules per photon and a space-time yield of 1.37 × 10-5 molecules per photon per mg. Additionally, EC-pod:ZnO exhibits significant antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) bacteria, showcasing its dual functionality as a potential photocatalyst and antimicrobial agent. This nature-inspired ZnO nanomaterial offers an economical, scalable, and sustainable solution for environmental and biomedical applications, highlighting its potential in wastewater treatment and microbial control.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activities of biogenic synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Mallotus philippinensis Mull. Arg.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 24;15(1):6541. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85264-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39994261 Free PMC article.
-
An Eco-friendly Approach to ZnO NP Synthesis Using Citrus reticulata Blanco Peel/Extract: Characterization and Antibacterial and Photocatalytic Activity.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 May 20;7(5):3014-3032. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c00079. Epub 2024 Apr 10. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 38597359
-
Exploring the multi-faceted potential: Synthesized ZnO nanostructure - Characterization, photocatalysis, and crucial biomedical applications.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 13;10(12):e32714. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32714. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39022102 Free PMC article.
-
Mycogenic Synthesis of Extracellular Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Xylaria acuta and Its Nanoantibiotic Potential.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Nov 2;15:8519-8536. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S271743. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33173290 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Pelargonium odoratissimum (L.) Aqueous Leaf Extract and Their Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Anti-inflammatory Activities.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;11(8):1444. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081444. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lellis B. Fávaro-Polonio C. Z. Pamphile J. A. Polonio J. C. Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019;3(2):275–290.
-
- Shimi A. K. Parvathiraj C. Kumari S. Dalal J. Kumar V. Wabaidur S. M. Alothman Z. A. Green synthesis of SrO nanoparticles using leaf extract of Albizia julibrissin and its recyclable photocatalytic activity: An eco-friendly approach for treatment of industrial wastewater. Environ. Sci.:Adv. 2022;1(5):849–861.
-
- Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications, ed. J. Dalal, A. Gupta, S. Korpal and V. N. Thakur, Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2024
-
- Kaur A. Kumar S. Kaur H. Lotey G. S. Singh P. P. Singh G. Kumar S. Dalal J. Bouzid G. Misra M. Pandey R. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation and antimicrobial activities of biogenic Co3O4 nanoparticles mediated by fenugreek: sustainable strategies. Mater. Adv. 2024;5(20):8111–8131.
-
- Ahmed S. F. Mofijur M. Nuzhat S. Chowdhury A. T. Rafa N. Uddin M. A. et al., Recent developments in physical, biological, chemical, and hybrid treatment techniques for removing emerging contaminants from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021;416:125912. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

