From cirrhosis to hepatogenous diabetes: risk factors and glycemic management
- PMID: 40395912
- PMCID: PMC12087320
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms/189834
From cirrhosis to hepatogenous diabetes: risk factors and glycemic management
Abstract
Introduction: Our study analyzed the risk factors associated with hepatogenous diabetes (HD) and compared glycemic control under various treatment modalities.
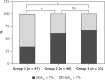
Material and methods: The multicenter study included 327 patients with HD, while 329 non-diabetic liver cirrhosis (LC) patients were selected as the control group for examining HD risk factors. Three groups of HD patients with HbA1c were distinguished based on their glucose-lowering treatment regimen to compare glycemic control.
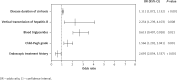
Results: The results indicated that longer disease duration of cirrhosis (OR = 1.111, 95% CI: 1.072-1.152, p < 0.001), vertical transmission of hepatitis B (OR = 2.254, 95% CI: 1.239-4.103, p = 0.008), a high Child-Pugh grade (OR = 1.566, 95% CI: 1.202-2.041, p = 0.001) and higher blood triglyceride levels (OR = 2.695, 95% CI: 2.054-3.537, p < 0.001) were independent risk factors for HD. A history of endoscopic treatment (OR = 0.615, 95% CI: 0.407-0.928, p = 0.021) was a protective factor for HD. Insulin or insulin in combination with oral hypoglycemic agents is more effective compared to oral medication alone (p1 < 0.05, p2 < 0.05).
Conclusions: The risk factors for HD include prolonged duration of LC, vertical transmission of hepatitis B, higher Child-Pugh grade, and elevated blood triglyceride levels. A history of endoscopic treatment was found to be a protective factor. Glycemic management was substantially enhanced among patients who received insulin therapy, either alone or combined with oral hypoglycemic drugs, as opposed to those who depended solely on oral hypoglycemic agents.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; hepatogenous diabetes; insulin resistance; liver cirrhosis; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright: © 2024 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatogenous Diabetes - A Report from Central India.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022 Mar-Apr;12(2):312-318. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2021.08.018. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35535090 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatogenous diabetes. Current views of an ancient problem.Ann Hepatol. 2009 Jan-Mar;8(1):13-20. Ann Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19221528 Review.
-
Hepatogenous Diabetes: An Underestimated Problem of Liver Cirrhosis.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Jul-Aug;22(4):552-559. doi: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_79_18. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30148106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the mechanisms of hepatogenous diabetes and its therapeutic perspectives.Life Sci. 2024 Sep 15;353:122934. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122934. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39089644 Review.
-
[Effects of long-acting insulin degludec on type 2 diabetic hemodialysis patients with poor glycemic control].Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2015;57(5):872-7. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2015. PMID: 26387380 Japanese.
References
-
- garcía-Compean D, Jaquez-Quintana JO, Maldonado-Garza H. Hepatogenous diabetes. Current views of an ancient problem. Ann Hepatol 2009; 8: 13-20. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Compean D, Gonzalez-Gonzalez JA, Lavalle-Gonzalez FJ, et al. . Current concepts in diabetes mellitus and chronic liver disease: clinical outcomes, hepatitis c virus association, and therapy. Dig Dis Sci 2016; 61: 371-80. - PubMed
-
- Orsi E, Grancini V, Menini S, et al. . Hepatogenous diabetes: Is it time to separate it from type 2 diabetes? Liver Int 2017; 37: 950-62. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee . 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022; 45 (Suppl 1): S17-38. - PubMed
-
- Chronic Disease Management Branch China Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Association . [Expert consensus on the management of diabetes mellitus in patients with liver cirrhosis]. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2022; 30: 846-58. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
