MiR-200a promotes the survival of cardiac cells and improves cardiac injury in chronic heart failure rats
- PMID: 40395913
- PMCID: PMC12087328
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2020.94500
MiR-200a promotes the survival of cardiac cells and improves cardiac injury in chronic heart failure rats
Abstract
Introduction: miRNAs play an important role in cardiovascular abnormalities such as heart failure. In the present work we evaluated the role of miR-200a in the condition of chronic heart failure and also the mechanism involved.
Material and methods: In the study 180 subjects, among whom 100 were reported for chronic heart failure and 80 as normal, were included. ELISA and qRT-PCR was done to evaluate levels of HMGB1 and miR-200a in subjects. The cardiac hemodynamics and functioning, oxidative stress and expression of mediators of inflammation were studied in rats with chronic heart failure induced after transfecting them with miR-200a or HMGB1. Luciferase activity was measured to establish any correlation between HMGB1 and miR-200a.
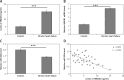
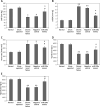
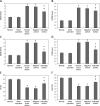
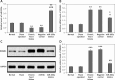
Results: The chronic heart failure patients included in the study showed suppressed levels of miR-200a and elevated HMGB1 compared to normal subjects. In chronic heart failure rats, the transfection of miR-200a attenuated the cardiac function and other hemodynamic parameters. In addition, improvement in oxidative stress as well as inflammatory mediators was observed. The outcomes also confirmed that HMGB1 was the potential target of miR-200a. It was also noted that upon transfection miR-200a resulted in suppression of protein as well as mRNA levels of HMGB1 in the cardiac tissue of chronic heart failure rats. Also overexpression of HMGB1 decreased the effects of miR-200a.
Conclusions: The outcomes indicate that miR-200a exerts a protective effect on cardiac cell injury via the HMGB1 pathway.
Keywords: HMGB1; chronic heart failure; miR-200a.
Copyright: © 2020 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
miR-129-5p improves cardiac function in rats with chronic heart failure through targeting HMGB1.Mamm Genome. 2019 Oct;30(9-10):276-288. doi: 10.1007/s00335-019-09817-0. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Mamm Genome. 2019. PMID: 31646380
-
The long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 modulates HCC cell proliferation through miR-200a-dependent HMGB1/RAGE regulation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Apr 12;36(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0519-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28403886 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA 101368/miR-200a axis modulates the migration of hepatocellular carcinoma through HMGB1/RAGE signaling.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(19-20):2349-2359. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1526599. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 30265210 Free PMC article.
-
miR-200a-5p regulates myocardial necroptosis induced by Se deficiency via targeting RNF11.Redox Biol. 2018 May;15:159-169. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.025. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 29248830 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-200a-3p Aggravates DOX-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Targeting PEG3 Through SIRT1/NF-κB Signal Pathway.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021 Apr;21(4):302-313. doi: 10.1007/s12012-020-09620-3. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33638775
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
